DynG2G: An Efficient Stochastic Graph Embedding Method for Temporal Graphs
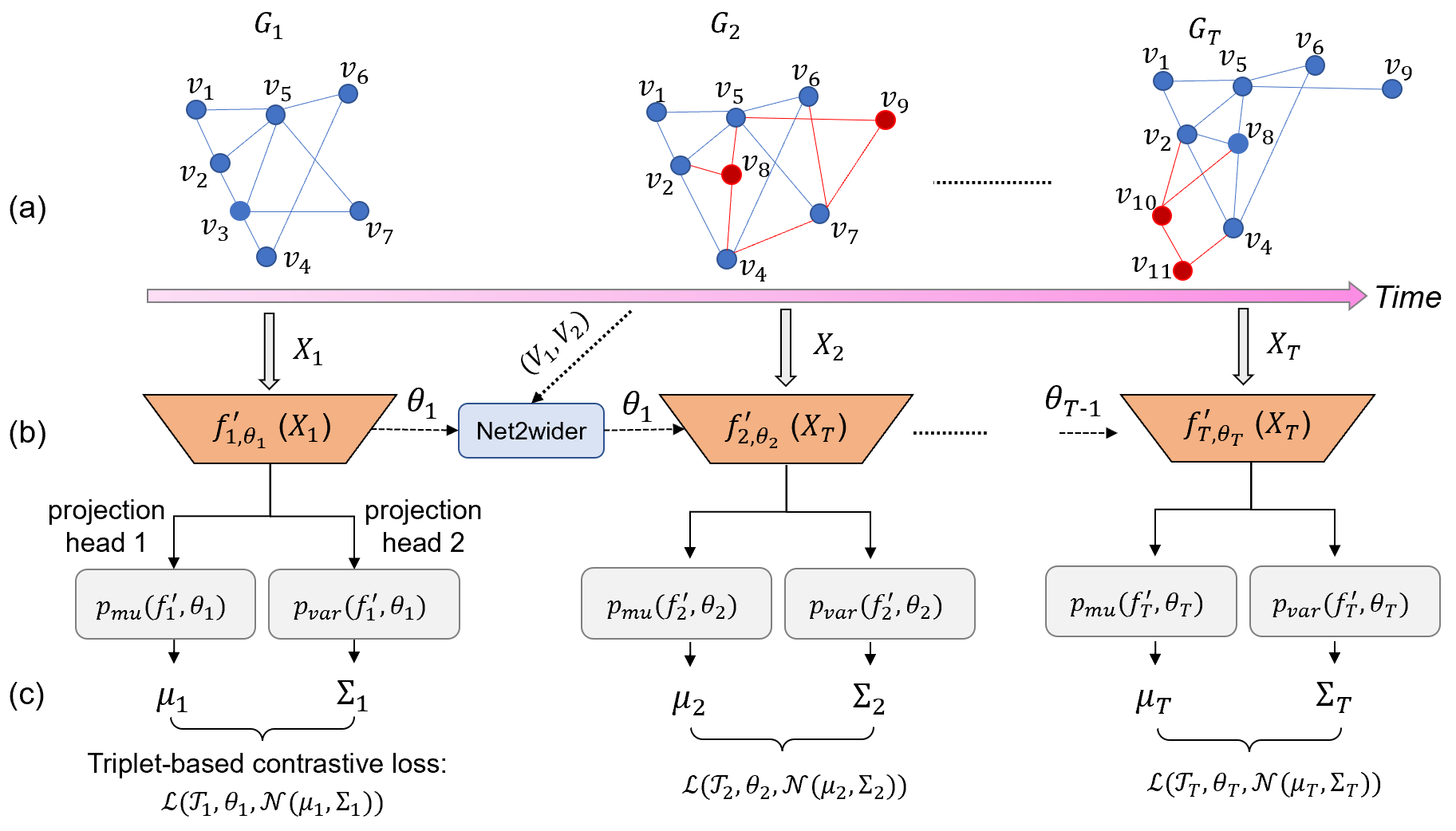
Dynamic graph embedding has gained great attention recently due to its capability of learning low dimensional graph representations for complex temporal graphs with high accuracy. However, recent advances mostly focus on learning node embeddings as deterministic "vectors" for static graphs yet disregarding the key graph temporal dynamics and the evolving uncertainties associated with node embedding in the latent space. In this work, we propose an efficient stochastic dynamic graph embedding method (DynG2G) that applies an inductive feed-forward encoder trained with node triplet-based contrastive loss. Every node per timestamp is encoded as a time-dependent probabilistic multivariate Gaussian distribution in the latent space, hence we can quantify the node embedding uncertainty on-the-fly. We adopted eight different benchmarks that represent diversity in size (from 96 nodes to 87,626 and from 13,398 edges to 4,870,863) and diversity in dynamics. We demonstrate via extensive experiments on these eight dynamic graph benchmarks that DynG2G achieves new state-of-the-art performance in capturing the underlying temporal node embeddings. We also demonstrate that DynG2G can predict the evolving node embedding uncertainty, which plays a crucial role in quantifying the intrinsic dimensionality of the dynamical system over time. We obtain a universal relation of the optimal embedding dimension, $L_o$, versus the effective dimensionality of uncertainty, $D_u$, and we infer that $L_o=D_u$ for all cases. This implies that the uncertainty quantification approach we employ in the DynG2G correctly captures the intrinsic dimensionality of the dynamics of such evolving graphs despite the diverse nature and composition of the graphs at each timestamp. Moreover, this $L_0 - D_u$ correlation provides a clear path to select adaptively the optimum embedding size at each timestamp by setting $L \ge D_u$.
PDF Abstract