Efficient and Generic Point Model for Lossless Point Cloud Attribute Compression
The past several years have witnessed the emergence of learned point cloud compression (PCC) techniques. However, current learning-based lossless point cloud attribute compression (PCAC) methods either suffer from high computational complexity or deteriorated compression performance. Moreover, the significant variations in point cloud scale and sparsity encountered in real-world applications make developing an all-in-one neural model a challenging task. In this paper, we propose PoLoPCAC, an efficient and generic lossless PCAC method that achieves high compression efficiency and strong generalizability simultaneously. We formulate lossless PCAC as the task of inferring explicit distributions of attributes from group-wise autoregressive priors. A progressive random grouping strategy is first devised to efficiently resolve the point cloud into groups, and then the attributes of each group are modeled sequentially from accumulated antecedents. A locality-aware attention mechanism is utilized to exploit prior knowledge from context windows in parallel. Since our method directly operates on points, it can naturally avoids distortion caused by voxelization, and can be executed on point clouds with arbitrary scale and density. Experiments show that our method can be instantly deployed once trained on a Synthetic 2k-ShapeNet dataset while enjoying continuous bit-rate reduction over the latest G-PCCv23 on various datasets (ShapeNet, ScanNet, MVUB, 8iVFB). Meanwhile, our method reports shorter coding time than G-PCCv23 on the majority of sequences with a lightweight model size (2.6MB), which is highly attractive for practical applications. Dataset, code and trained model are available at https://github.com/I2-Multimedia-Lab/PoLoPCAC.
PDF Abstract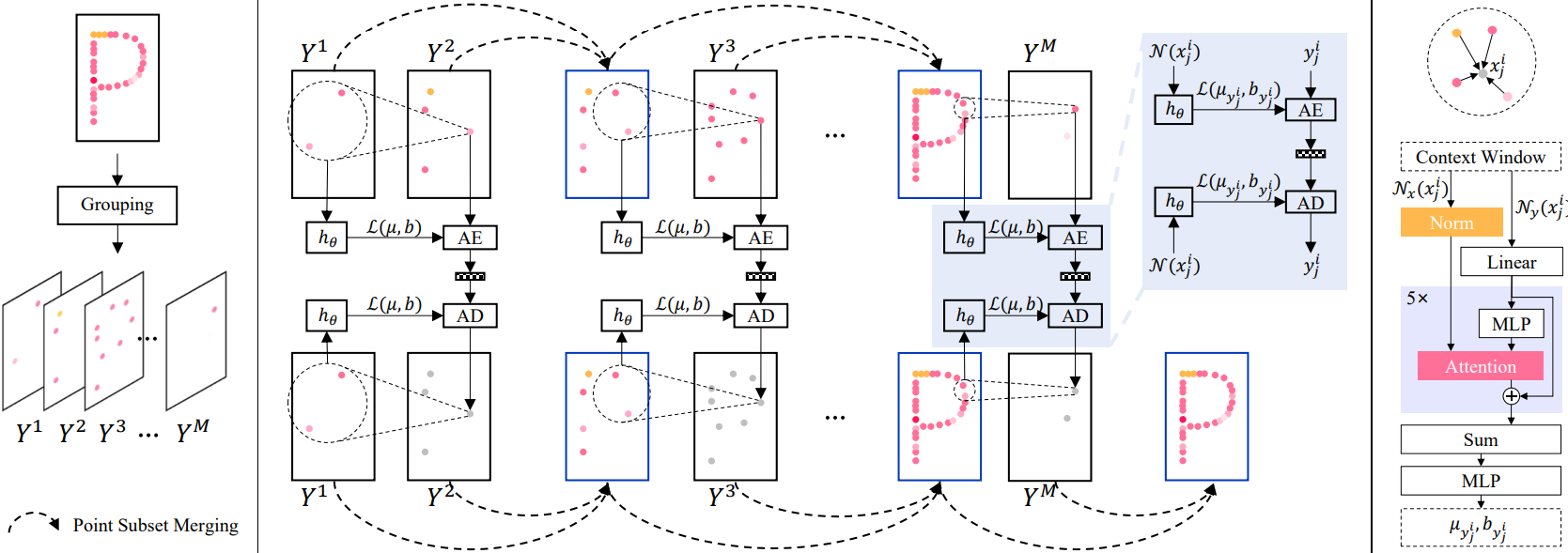


 ShapeNet
ShapeNet
 ScanNet
ScanNet
 SemanticKITTI
SemanticKITTI