End-to-End Dense Video Captioning with Parallel Decoding
Dense video captioning aims to generate multiple associated captions with their temporal locations from the video. Previous methods follow a sophisticated "localize-then-describe" scheme, which heavily relies on numerous hand-crafted components. In this paper, we proposed a simple yet effective framework for end-to-end dense video captioning with parallel decoding (PDVC), by formulating the dense caption generation as a set prediction task. In practice, through stacking a newly proposed event counter on the top of a transformer decoder, the PDVC precisely segments the video into a number of event pieces under the holistic understanding of the video content, which effectively increases the coherence and readability of predicted captions. Compared with prior arts, the PDVC has several appealing advantages: (1) Without relying on heuristic non-maximum suppression or a recurrent event sequence selection network to remove redundancy, PDVC directly produces an event set with an appropriate size; (2) In contrast to adopting the two-stage scheme, we feed the enhanced representations of event queries into the localization head and caption head in parallel, making these two sub-tasks deeply interrelated and mutually promoted through the optimization; (3) Without bells and whistles, extensive experiments on ActivityNet Captions and YouCook2 show that PDVC is capable of producing high-quality captioning results, surpassing the state-of-the-art two-stage methods when its localization accuracy is on par with them. Code is available at https://github.com/ttengwang/PDVC.
PDF Abstract ICCV 2021 PDF ICCV 2021 Abstract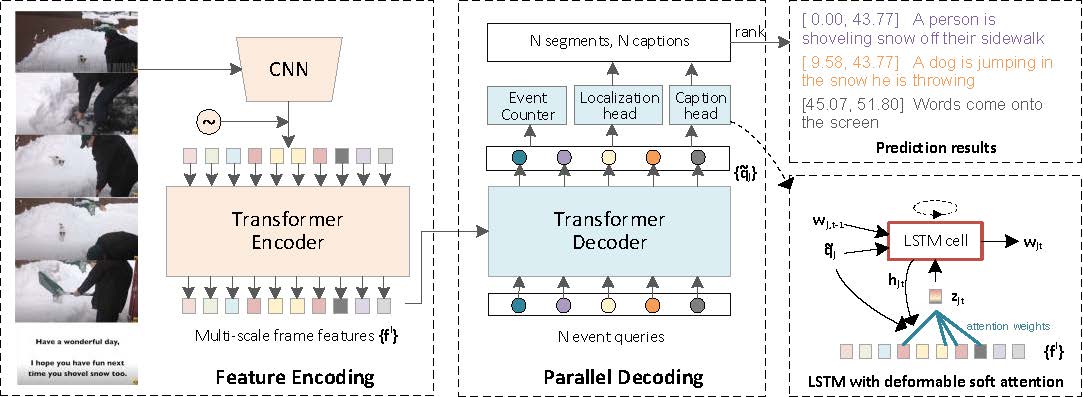




 ActivityNet Captions
ActivityNet Captions
 YouCook2
YouCook2
