Enhancing the Performance of Automated Grade Prediction in MOOC using Graph Representation Learning
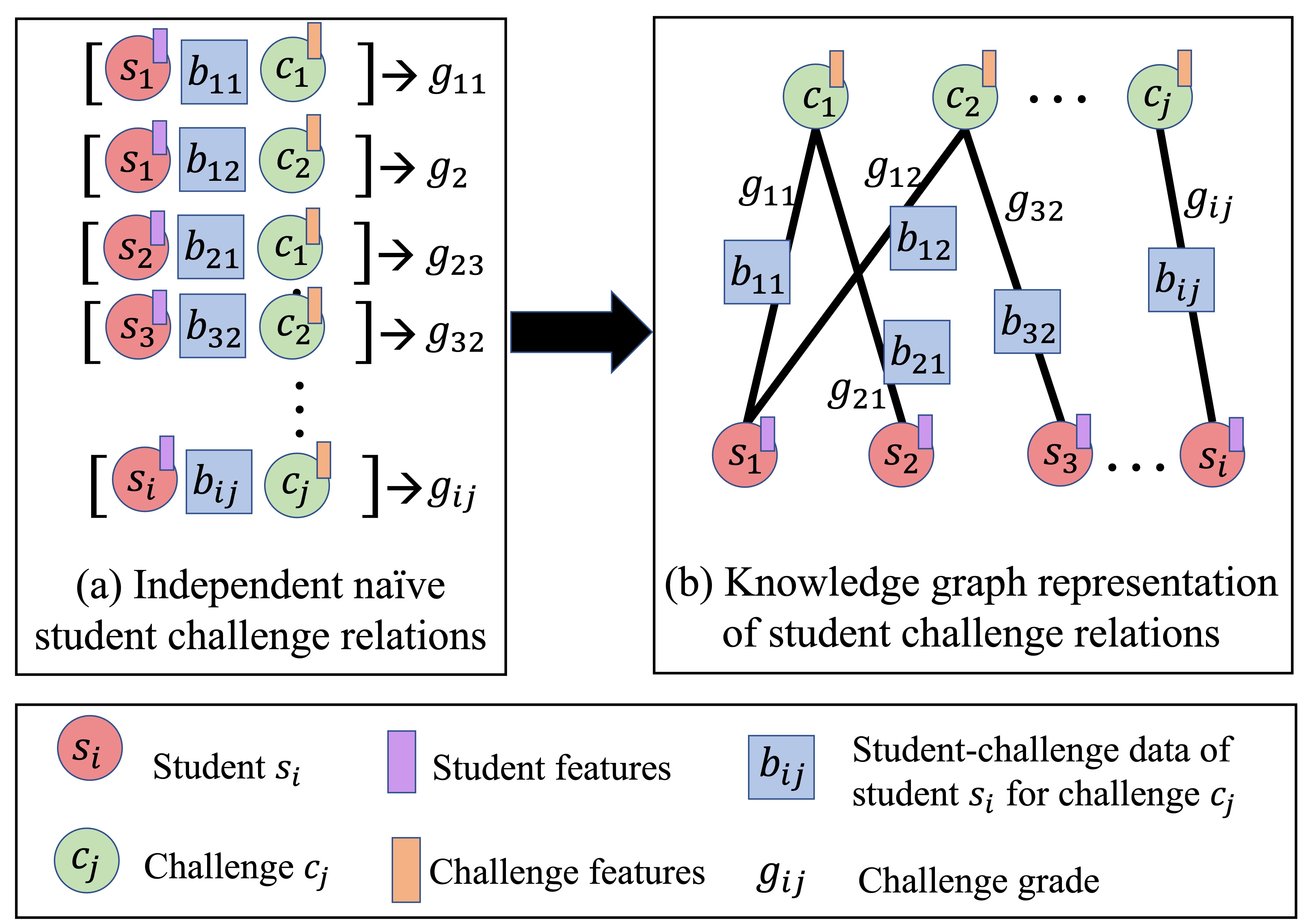
In recent years, Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) have gained significant traction as a rapidly growing phenomenon in online learning. Unlike traditional classrooms, MOOCs offer a unique opportunity to cater to a diverse audience from different backgrounds and geographical locations. Renowned universities and MOOC-specific providers, such as Coursera, offer MOOC courses on various subjects. Automated assessment tasks like grade and early dropout predictions are necessary due to the high enrollment and limited direct interaction between teachers and learners. However, current automated assessment approaches overlook the structural links between different entities involved in the downstream tasks, such as the students and courses. Our hypothesis suggests that these structural relationships, manifested through an interaction graph, contain valuable information that can enhance the performance of the task at hand. To validate this, we construct a unique knowledge graph for a large MOOC dataset, which will be publicly available to the research community. Furthermore, we utilize graph embedding techniques to extract latent structural information encoded in the interactions between entities in the dataset. These techniques do not require ground truth labels and can be utilized for various tasks. Finally, by combining entity-specific features, behavioral features, and extracted structural features, we enhance the performance of predictive machine learning models in student assignment grade prediction. Our experiments demonstrate that structural features can significantly improve the predictive performance of downstream assessment tasks. The code and data are available in \url{https://github.com/DSAatUSU/MOOPer_grade_prediction}
PDF Abstract