Exploring Attention-Aware Network Resource Allocation for Customized Metaverse Services
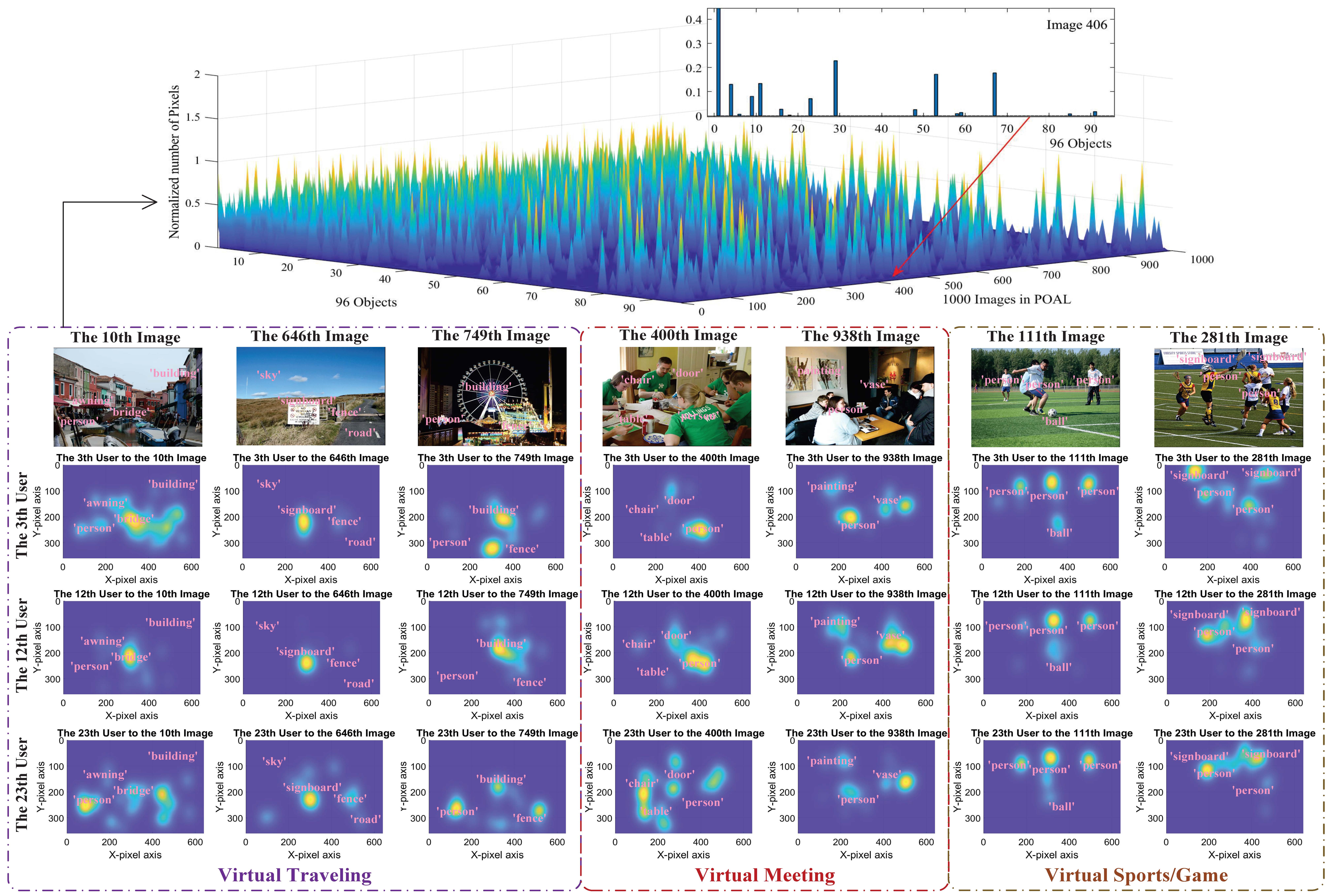
Emerging with the support of computing and communications technologies, Metaverse is expected to bring users unprecedented service experiences. However, the increase in the number of Metaverse users places a heavy demand on network resources, especially for Metaverse services that are based on graphical extended reality and require rendering a plethora of virtual objects. To make efficient use of network resources and improve the Quality-of-Experience (QoE), we design an attention-aware network resource allocation scheme to achieve customized Metaverse services. The aim is to allocate more network resources to virtual objects in which users are more interested. We first discuss several key techniques related to Metaverse services, including QoE analysis, eye-tracking, and remote rendering. We then review existing datasets and propose the user-object-attention level (UOAL) dataset that contains the ground truth attention of 30 users to 96 objects in 1,000 images. A tutorial on how to use UOAL is presented. With the help of UOAL, we propose an attention-aware network resource allocation algorithm that has two steps, i.e., attention prediction and QoE maximization. Specially, we provide an overview of the designs of two types of attention prediction methods, i.e., interest-aware and time-aware prediction. By using the predicted user-object-attention values, network resources such as the rendering capacity of edge devices can be allocated optimally to maximize the QoE. Finally, we propose promising research directions related to Metaverse services.
PDF Abstract