Graduated Non-Convexity for Robust Spatial Perception: From Non-Minimal Solvers to Global Outlier Rejection
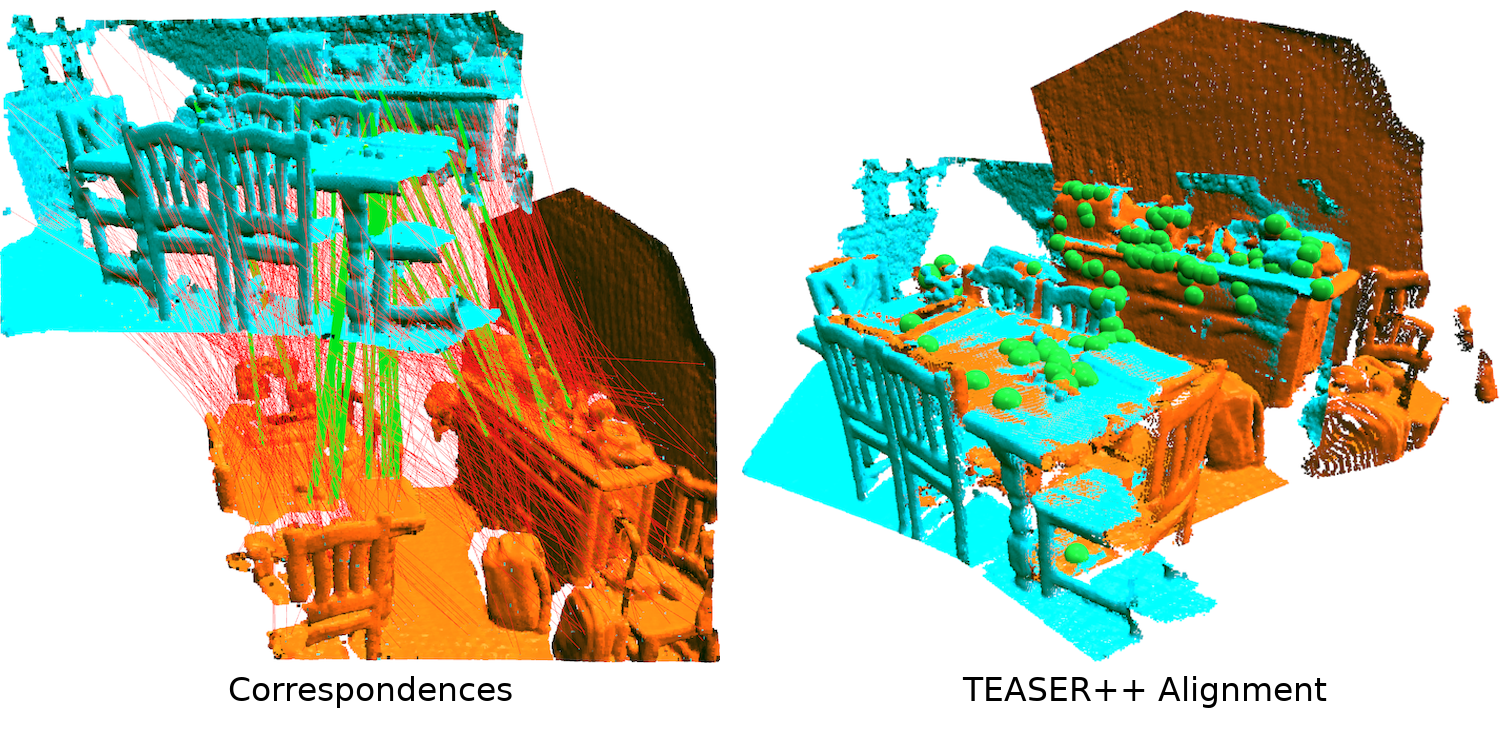
Semidefinite Programming (SDP) and Sums-of-Squares (SOS) relaxations have led to certifiably optimal non-minimal solvers for several robotics and computer vision problems. However, most non-minimal solvers rely on least-squares formulations, and, as a result, are brittle against outliers. While a standard approach to regain robustness against outliers is to use robust cost functions, the latter typically introduce other non-convexities, preventing the use of existing non-minimal solvers. In this paper, we enable the simultaneous use of non-minimal solvers and robust estimation by providing a general-purpose approach for robust global estimation, which can be applied to any problem where a non-minimal solver is available for the outlier-free case. To this end, we leverage the Black-Rangarajan duality between robust estimation and outlier processes (which has been traditionally applied to early vision problems), and show that graduated non-convexity (GNC) can be used in conjunction with non-minimal solvers to compute robust solutions, without requiring an initial guess. Although GNC's global optimality cannot be guaranteed, we demonstrate the empirical robustness of the resulting robust non-minimal solvers in applications, including point cloud and mesh registration, pose graph optimization, and image-based object pose estimation (also called shape alignment). Our solvers are robust to 70-80% of outliers, outperform RANSAC, are more accurate than specialized local solvers, and faster than specialized global solvers. We also propose the first certifiably optimal non-minimal solver for shape alignment using SOS relaxation.
PDF Abstract