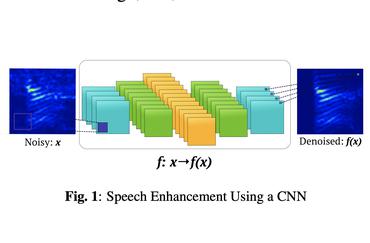
Incorporating Multi-Target in Multi-Stage Speech Enhancement Model for Better Generalization
Recent single-channel speech enhancement methods based on deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved remarkable results, but there are still generalization problems in real scenes. Like other data-driven methods, DNN-based speech enhancement models produce significant performance degradation on untrained data. In this study, we make full use of the contribution of multi-target joint learning to the model generalization capability, and propose a lightweight and low-computing dilated convolutional network (DCN) model for a more robust speech denoising task. Our goal is to integrate the masking target, the mapping target, and the parameters of the traditional speech enhancement estimator into a DCN model to maximize their complementary advantages. To do this, we build a multi-stage learning framework to deal with multiple targets in stages to achieve their joint learning, namely `MT-in-MS'. Our experimental results show that compared with the state-of-the-art time domain and time-frequency domain models, this proposed low-cost DCN model can achieve better generalization performance in speaker, noise, and channel mismatch cases.
PDF Abstract