LEAD: Learning Decomposition for Source-free Universal Domain Adaptation
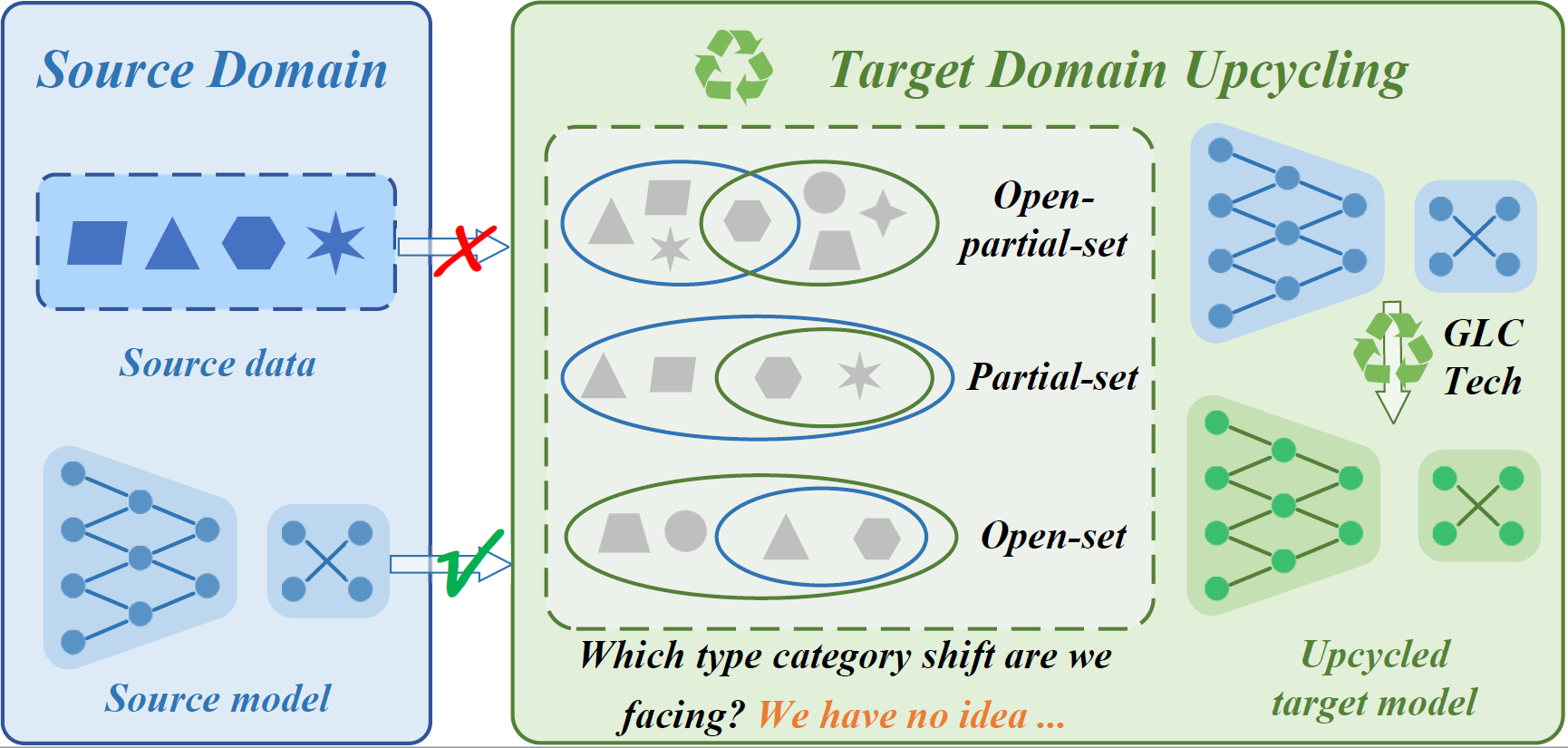
Universal Domain Adaptation (UniDA) targets knowledge transfer in the presence of both covariate and label shifts. Recently, Source-free Universal Domain Adaptation (SF-UniDA) has emerged to achieve UniDA without access to source data, which tends to be more practical due to data protection policies. The main challenge lies in determining whether covariate-shifted samples belong to target-private unknown categories. Existing methods tackle this either through hand-crafted thresholding or by developing time-consuming iterative clustering strategies. In this paper, we propose a new idea of LEArning Decomposition (LEAD), which decouples features into source-known and -unknown components to identify target-private data. Technically, LEAD initially leverages the orthogonal decomposition analysis for feature decomposition. Then, LEAD builds instance-level decision boundaries to adaptively identify target-private data. Extensive experiments across various UniDA scenarios have demonstrated the effectiveness and superiority of LEAD. Notably, in the OPDA scenario on VisDA dataset, LEAD outperforms GLC by 3.5% overall H-score and reduces 75% time to derive pseudo-labeling decision boundaries. Besides, LEAD is also appealing in that it is complementary to most existing methods. The code is available at https://github.com/ispc-lab/LEAD.
PDF AbstractCode
Datasets
| Task | Dataset | Model | Metric Name | Metric Value | Global Rank | Benchmark |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Universal Domain Adaptation | DomainNet | LEAD | H-Score | 50.8 | # 5 | |
| Source-free | yes | # 1 | ||||
| Universal Domain Adaptation | Office-31 | LEAD | H-score | 87.8 | # 5 | |
| Source-Free | yes | # 1 | ||||
| Universal Domain Adaptation | Office-Home | LEAD | H-Score | 75.0 | # 7 | |
| Source-free | yes | # 1 | ||||
| Universal Domain Adaptation | VisDA2017 | LEAD | H-score | 76.6 | # 1 | |
| Source-free | yes | # 1 |








 Office-Home
Office-Home
 DomainNet
DomainNet
 Office-31
Office-31
 VisDA-2017
VisDA-2017
