Learning Dual Memory Dictionaries for Blind Face Restoration
To improve the performance of blind face restoration, recent works mainly treat the two aspects, i.e., generic and specific restoration, separately. In particular, generic restoration attempts to restore the results through general facial structure prior, while on the one hand, cannot generalize to real-world degraded observations due to the limited capability of direct CNNs' mappings in learning blind restoration, and on the other hand, fails to exploit the identity-specific details. On the contrary, specific restoration aims to incorporate the identity features from the reference of the same identity, in which the requirement of proper reference severely limits the application scenarios. Generally, it is a challenging and intractable task to improve the photo-realistic performance of blind restoration and adaptively handle the generic and specific restoration scenarios with a single unified model. Instead of implicitly learning the mapping from a low-quality image to its high-quality counterpart, this paper suggests a DMDNet by explicitly memorizing the generic and specific features through dual dictionaries. First, the generic dictionary learns the general facial priors from high-quality images of any identity, while the specific dictionary stores the identity-belonging features for each person individually. Second, to handle the degraded input with or without specific reference, dictionary transform module is suggested to read the relevant details from the dual dictionaries which are subsequently fused into the input features. Finally, multi-scale dictionaries are leveraged to benefit the coarse-to-fine restoration. Moreover, a new high-quality dataset, termed CelebRef-HQ, is constructed to promote the exploration of specific face restoration in the high-resolution space.
PDF Abstract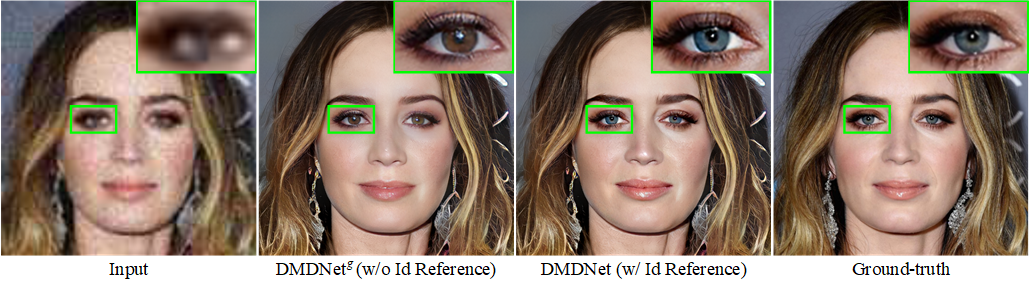


 FFHQ
FFHQ
 CelebA-HQ
CelebA-HQ