Leveraging Recursive Gumbel-Max Trick for Approximate Inference in Combinatorial Spaces
Structured latent variables allow incorporating meaningful prior knowledge into deep learning models. However, learning with such variables remains challenging because of their discrete nature. Nowadays, the standard learning approach is to define a latent variable as a perturbed algorithm output and to use a differentiable surrogate for training. In general, the surrogate puts additional constraints on the model and inevitably leads to biased gradients. To alleviate these shortcomings, we extend the Gumbel-Max trick to define distributions over structured domains. We avoid the differentiable surrogates by leveraging the score function estimators for optimization. In particular, we highlight a family of recursive algorithms with a common feature we call stochastic invariant. The feature allows us to construct reliable gradient estimates and control variates without additional constraints on the model. In our experiments, we consider various structured latent variable models and achieve results competitive with relaxation-based counterparts.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2021 PDF NeurIPS 2021 Abstract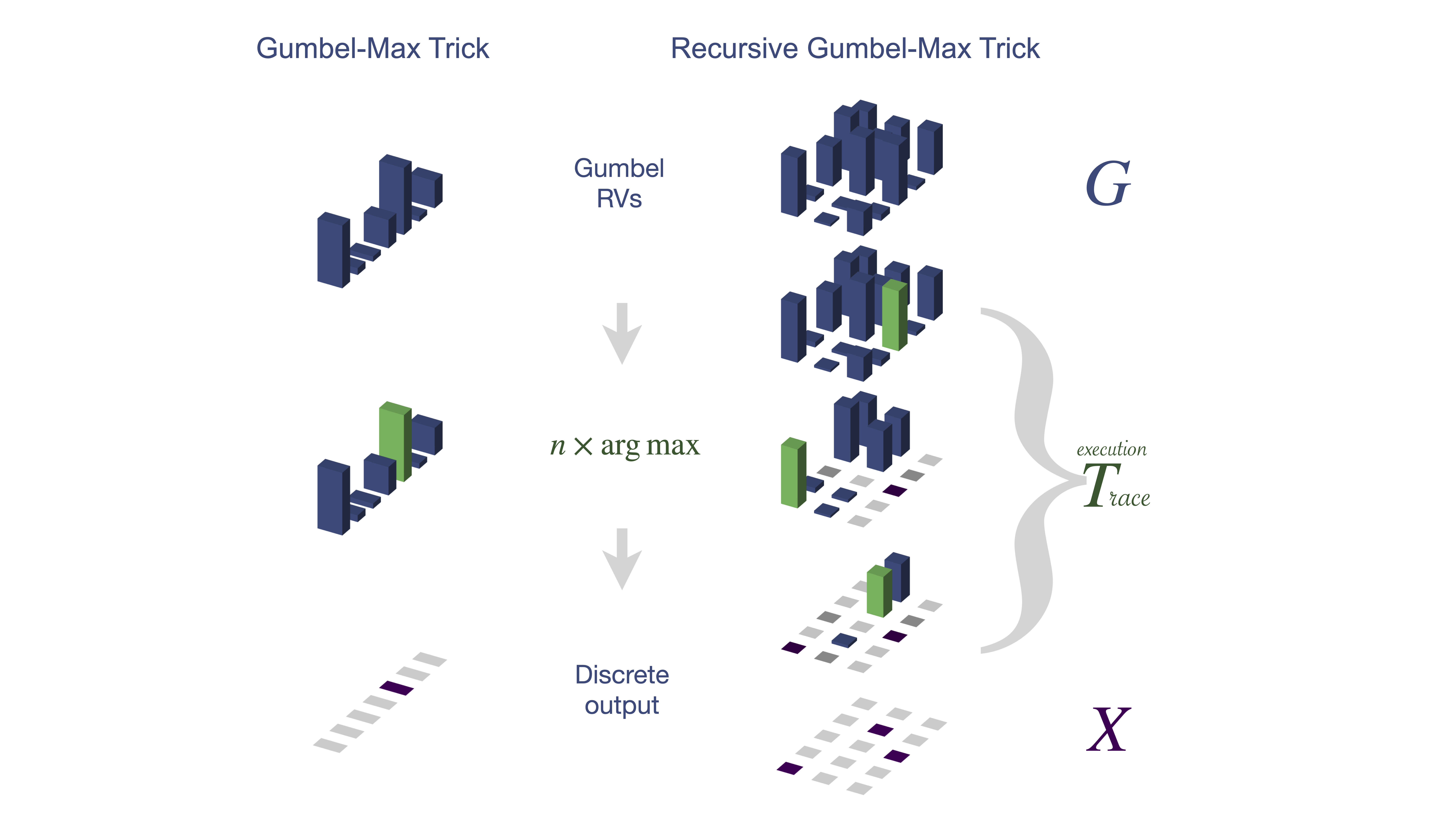

 ListOps
ListOps