Mitigating Adversarial Effects Through Randomization
Convolutional neural networks have demonstrated high accuracy on various tasks in recent years. However, they are extremely vulnerable to adversarial examples. For example, imperceptible perturbations added to clean images can cause convolutional neural networks to fail. In this paper, we propose to utilize randomization at inference time to mitigate adversarial effects. Specifically, we use two randomization operations: random resizing, which resizes the input images to a random size, and random padding, which pads zeros around the input images in a random manner. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed randomization method is very effective at defending against both single-step and iterative attacks. Our method provides the following advantages: 1) no additional training or fine-tuning, 2) very few additional computations, 3) compatible with other adversarial defense methods. By combining the proposed randomization method with an adversarially trained model, it achieves a normalized score of 0.924 (ranked No.2 among 107 defense teams) in the NIPS 2017 adversarial examples defense challenge, which is far better than using adversarial training alone with a normalized score of 0.773 (ranked No.56). The code is public available at https://github.com/cihangxie/NIPS2017_adv_challenge_defense.
PDF Abstract ICLR 2018 PDF ICLR 2018 Abstract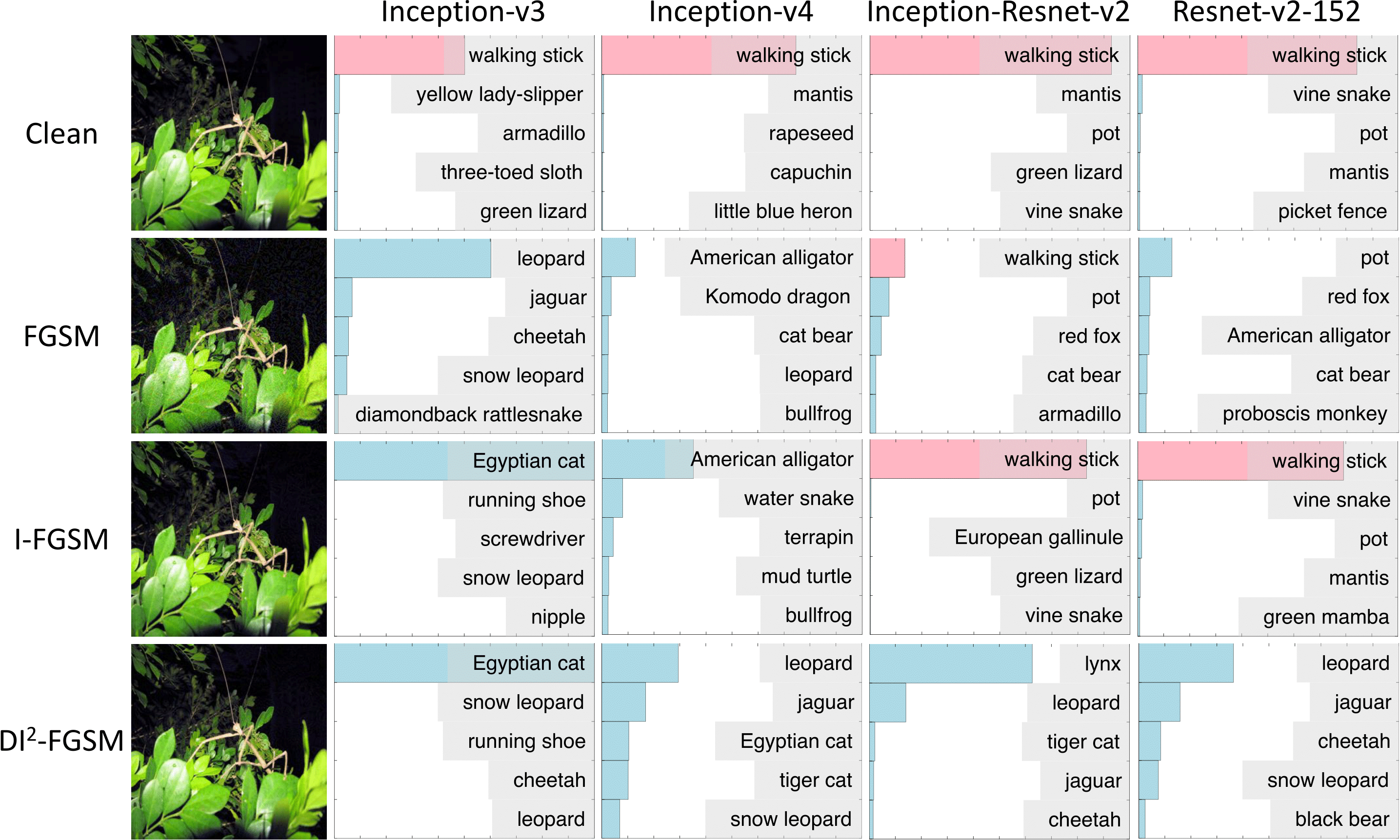


 ImageNet
ImageNet