Multi-Objective De Novo Drug Design with Conditional Graph Generative Model
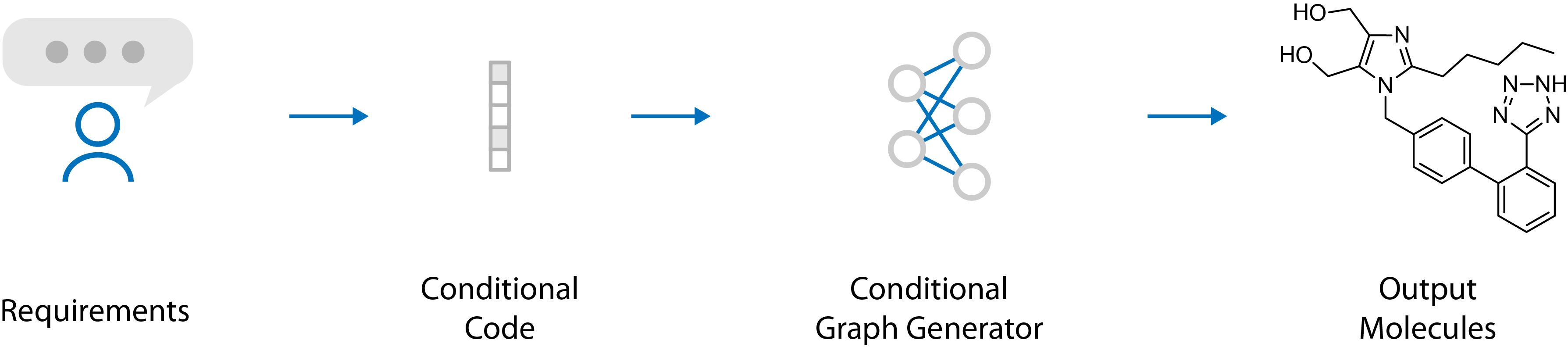
Recently, deep generative models have revealed itself as a promising way of performing de novo molecule design. However, previous research has focused mainly on generating SMILES strings instead of molecular graphs. Although current graph generative models are available, they are often too general and computationally expensive, which restricts their application to molecules with small sizes. In this work, a new de novo molecular design framework is proposed based on a type sequential graph generators that do not use atom level recurrent units. Compared with previous graph generative models, the proposed method is much more tuned for molecule generation and have been scaled up to cover significantly larger molecules in the ChEMBL database. It is shown that the graph-based model outperforms SMILES based models in a variety of metrics, especially in the rate of valid outputs. For the application of drug design tasks, conditional graph generative model is employed. This method offers higher flexibility compared to previous fine-tuning based approach and is suitable for generation based on multiple objectives. This approach is applied to solve several drug design problems, including the generation of compounds containing a given scaffold, generation of compounds with specific drug-likeness and synthetic accessibility requirements, as well as generating dual inhibitors against JNK3 and GSK3$\beta$. Results show high enrichment rates for outputs satisfying the given requirements.
PDF Abstract