Multiple Physics Pretraining for Physical Surrogate Models
We introduce multiple physics pretraining (MPP), an autoregressive task-agnostic pretraining approach for physical surrogate modeling. MPP involves training large surrogate models to predict the dynamics of multiple heterogeneous physical systems simultaneously by learning features that are broadly useful across diverse physical tasks. In order to learn effectively in this setting, we introduce a shared embedding and normalization strategy that projects the fields of multiple systems into a single shared embedding space. We validate the efficacy of our approach on both pretraining and downstream tasks over a broad fluid mechanics-oriented benchmark. We show that a single MPP-pretrained transformer is able to match or outperform task-specific baselines on all pretraining sub-tasks without the need for finetuning. For downstream tasks, we demonstrate that finetuning MPP-trained models results in more accurate predictions across multiple time-steps on new physics compared to training from scratch or finetuning pretrained video foundation models. We open-source our code and model weights trained at multiple scales for reproducibility and community experimentation.
PDF Abstract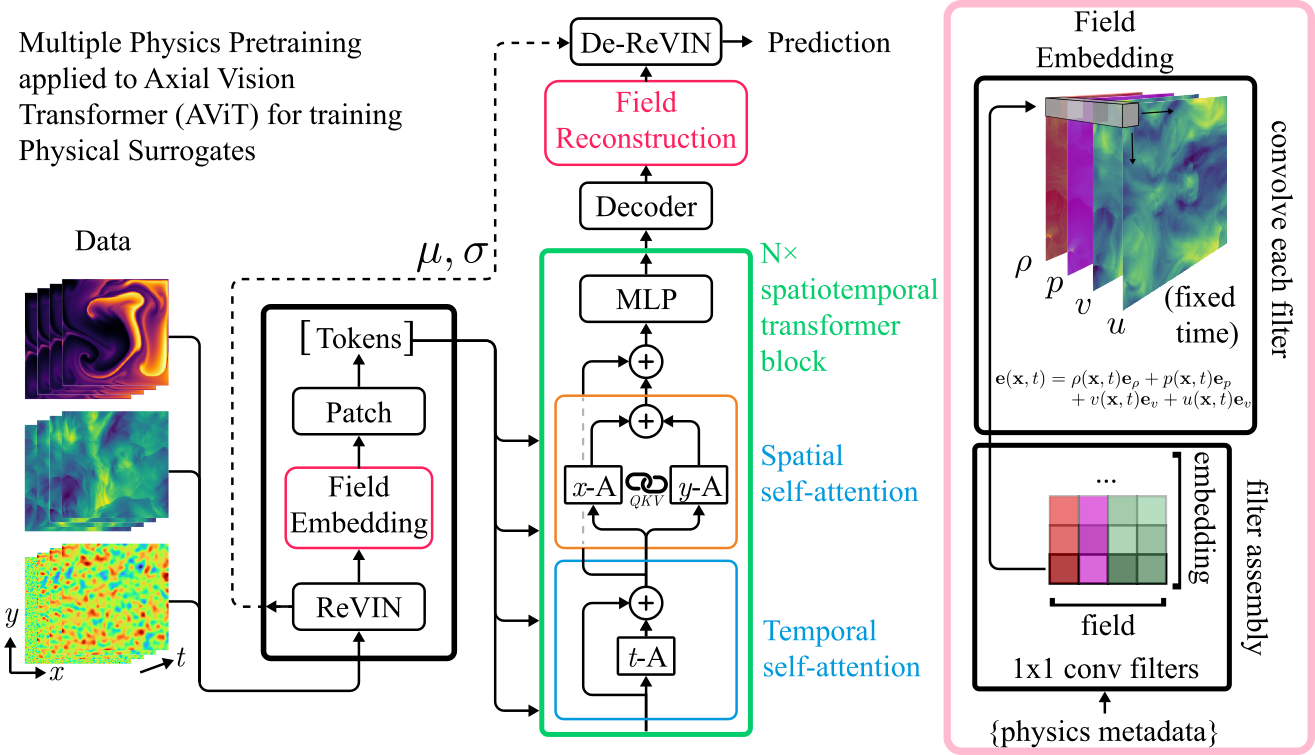

 PDEBench - Benchmark for Scientific Machine Learning
PDEBench - Benchmark for Scientific Machine Learning