Pseudo-Inverted Bottleneck Convolution for DARTS Search Space
Differentiable Architecture Search (DARTS) has attracted considerable attention as a gradient-based neural architecture search method. Since the introduction of DARTS, there has been little work done on adapting the action space based on state-of-art architecture design principles for CNNs. In this work, we aim to address this gap by incrementally augmenting the DARTS search space with micro-design changes inspired by ConvNeXt and studying the trade-off between accuracy, evaluation layer count, and computational cost. We introduce the Pseudo-Inverted Bottleneck Conv (PIBConv) block intending to reduce the computational footprint of the inverted bottleneck block proposed in ConvNeXt. Our proposed architecture is much less sensitive to evaluation layer count and outperforms a DARTS network with similar size significantly, at layer counts as small as 2. Furthermore, with less layers, not only does it achieve higher accuracy with lower computational footprint (measured in GMACs) and parameter count, GradCAM comparisons show that our network can better detect distinctive features of target objects compared to DARTS. Code is available from https://github.com/mahdihosseini/PIBConv.
PDF Abstract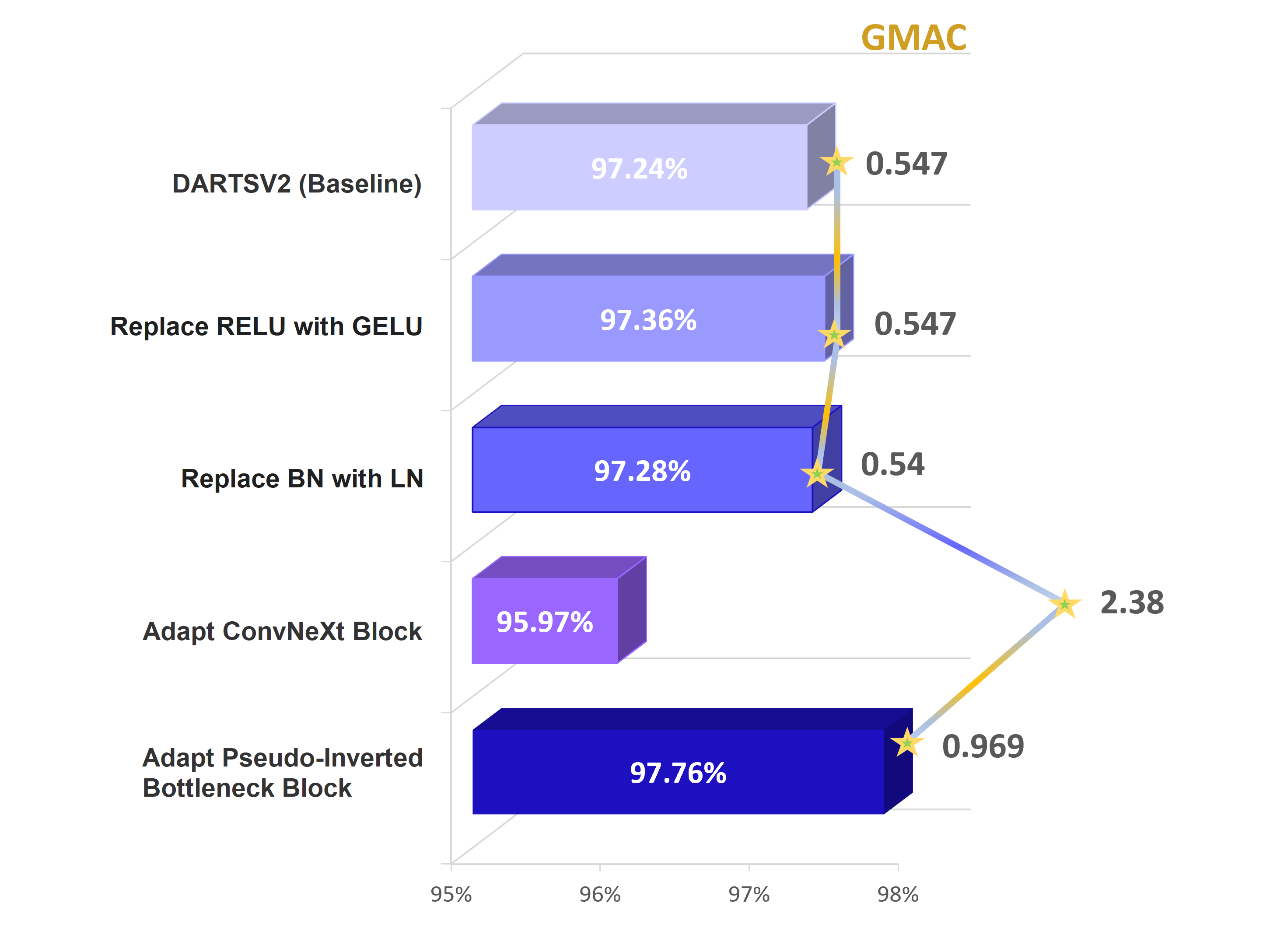


 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10