Recurrent Multigraph Integrator Network for Predicting the Evolution of Population-Driven Brain Connectivity Templates
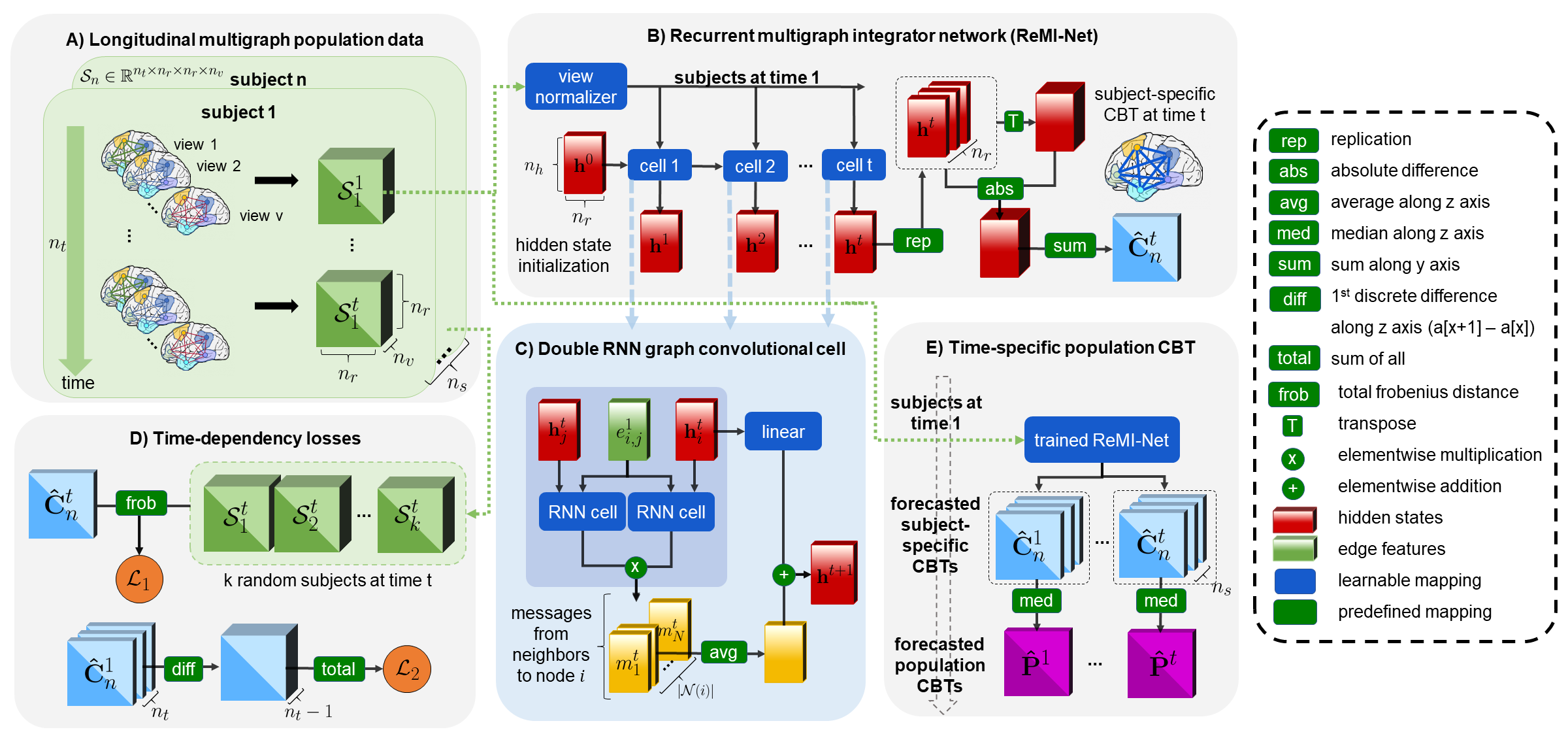
Learning how to estimate a connectional brain template(CBT) from a population of brain multigraphs, where each graph (e.g., functional) quantifies a particular relationship between pairs of brain regions of interest (ROIs), allows to pin down the unique connectivity patterns shared across individuals. Specifically, a CBT is viewed as an integral representation of a set of highly heterogeneous graphs and ideally meeting the centeredness (i.e., minimum distance to all graphs in the population) and discriminativeness (i.e., distinguishes the healthy from the disordered population) criteria. So far, existing works have been limited to only integrating and fusing a population of brain multigraphs acquired at a single timepoint. In this paper, we unprecedentedly tackle the question: Given a baseline multigraph population, can we learn how to integrate and forecast its CBT representations at follow-up timepoints? Addressing such question is of paramount in predicting common alternations across healthy and disordered populations. To fill this gap, we propose Recurrent Multigraph Integrator Network (ReMI-Net), the first graph recurrent neural network which infers the baseline CBT of an input population t1 and predicts its longitudinal evolution over time (ti > t1). Our ReMI-Net is composed of recurrent neural blocks with graph convolutional layers using a cross-node message passing to first learn hidden-states embeddings of each CBT node (i.e., brain region of interest) and then predict its evolution at the consecutive timepoint. Moreover, we design a novel time-dependent loss to regularize the CBT evolution trajectory over time and further introduce a cyclic recursion and learnable normalization layer to generate well-centered CBTs from time-dependent hidden-state embeddings. Finally, we derive the CBT adjacency matrix from the learned hidden state graph representation.
PDF Abstract