Refining Minimax Regret for Unsupervised Environment Design
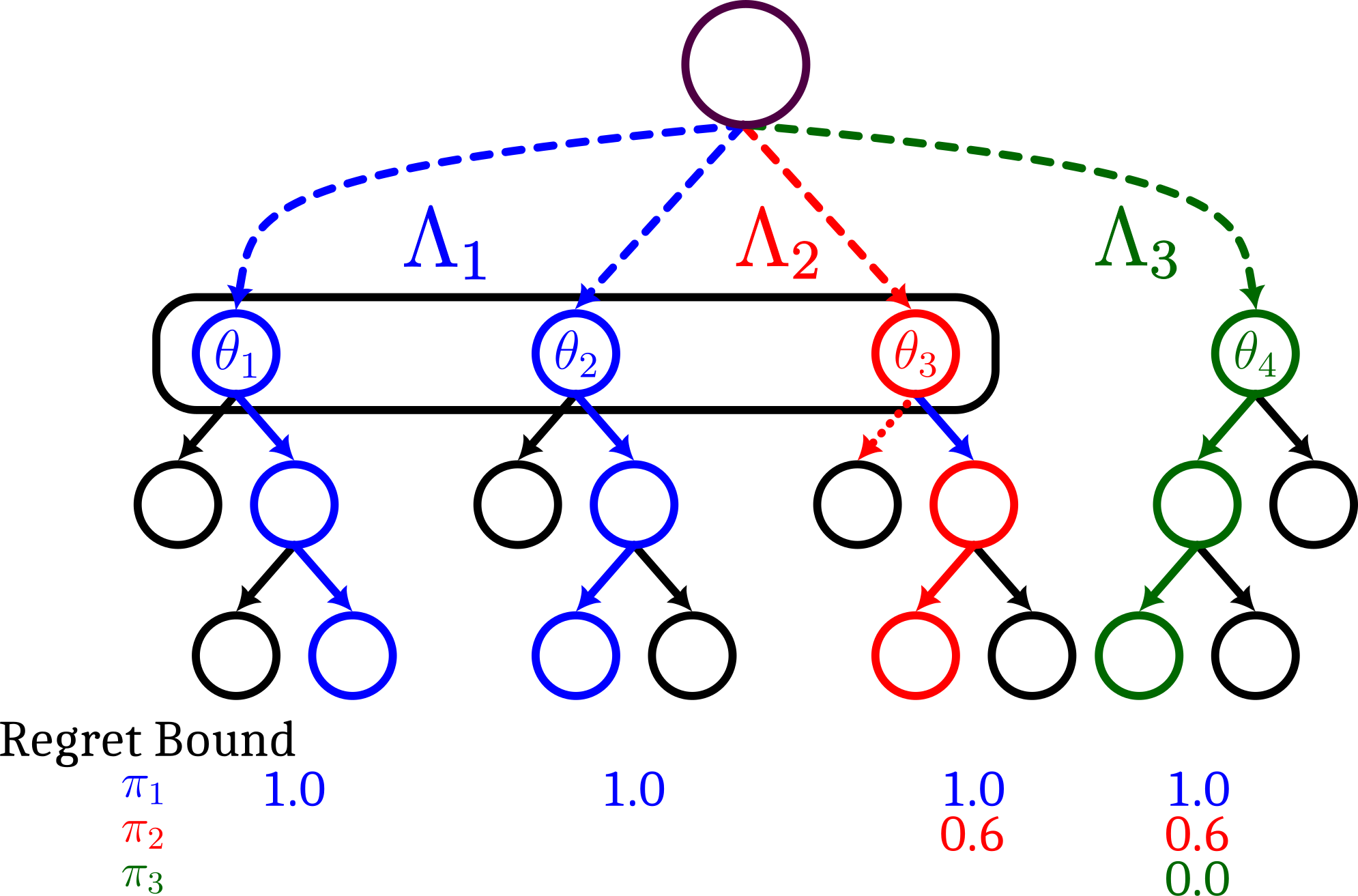
In unsupervised environment design, reinforcement learning agents are trained on environment configurations (levels) generated by an adversary that maximises some objective. Regret is a commonly used objective that theoretically results in a minimax regret (MMR) policy with desirable robustness guarantees; in particular, the agent's maximum regret is bounded. However, once the agent reaches this regret bound on all levels, the adversary will only sample levels where regret cannot be further reduced. Although there are possible performance improvements to be made outside of these regret-maximising levels, learning stagnates. In this work, we introduce Bayesian level-perfect MMR (BLP), a refinement of the minimax regret objective that overcomes this limitation. We formally show that solving for this objective results in a subset of MMR policies, and that BLP policies act consistently with a Perfect Bayesian policy over all levels. We further introduce an algorithm, ReMiDi, that results in a BLP policy at convergence. We empirically demonstrate that training on levels from a minimax regret adversary causes learning to prematurely stagnate, but that ReMiDi continues learning.
PDF Abstract