Scalars are universal: Equivariant machine learning, structured like classical physics
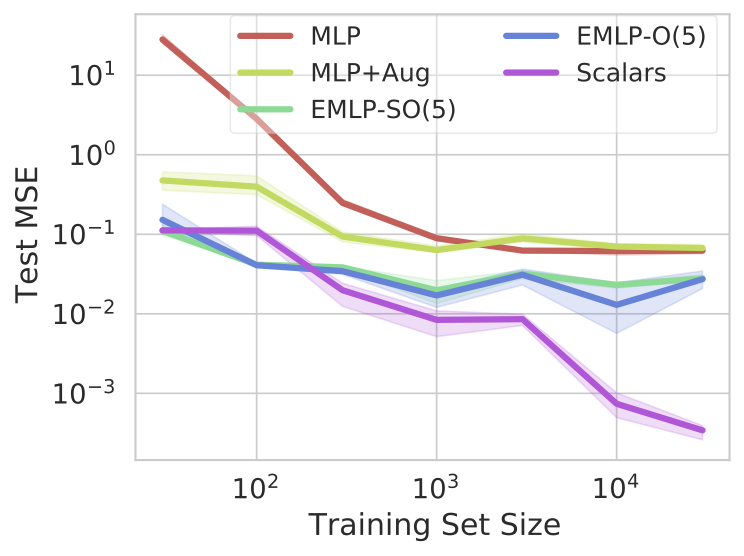
There has been enormous progress in the last few years in designing neural networks that respect the fundamental symmetries and coordinate freedoms of physical law. Some of these frameworks make use of irreducible representations, some make use of high-order tensor objects, and some apply symmetry-enforcing constraints. Different physical laws obey different combinations of fundamental symmetries, but a large fraction (possibly all) of classical physics is equivariant to translation, rotation, reflection (parity), boost (relativity), and permutations. Here we show that it is simple to parameterize universally approximating polynomial functions that are equivariant under these symmetries, or under the Euclidean, Lorentz, and Poincar\'e groups, at any dimensionality $d$. The key observation is that nonlinear O($d$)-equivariant (and related-group-equivariant) functions can be universally expressed in terms of a lightweight collection of scalars -- scalar products and scalar contractions of the scalar, vector, and tensor inputs. We complement our theory with numerical examples that show that the scalar-based method is simple, efficient, and scalable.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2021 PDF NeurIPS 2021 Abstract