Unsupervised Representation Learning for Binary Networks by Joint Classifier Learning
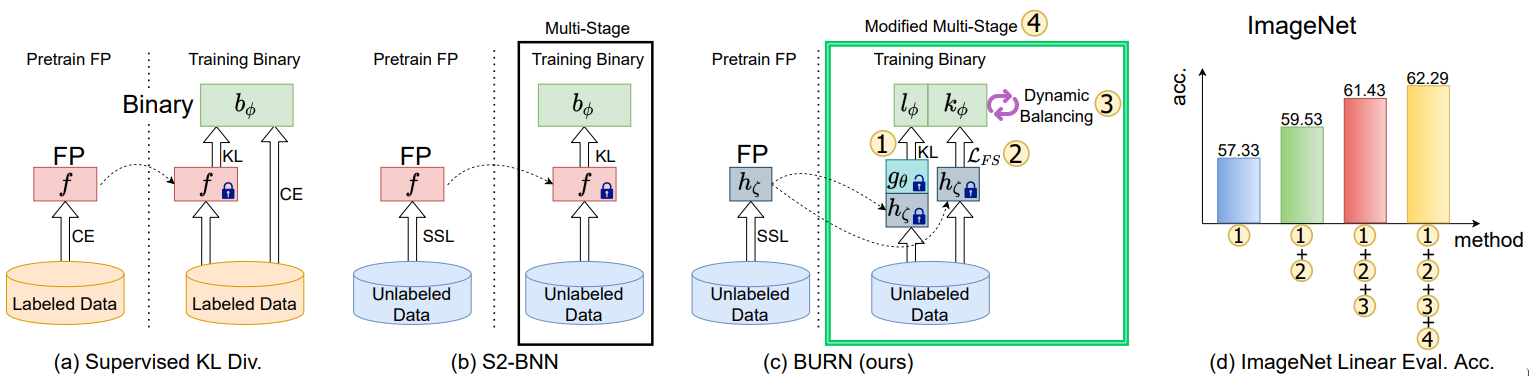
Self-supervised learning is a promising unsupervised learning framework that has achieved success with large floating point networks. But such networks are not readily deployable to edge devices. To accelerate deployment of models with the benefit of unsupervised representation learning to such resource limited devices for various downstream tasks, we propose a self-supervised learning method for binary networks that uses a moving target network. In particular, we propose to jointly train a randomly initialized classifier, attached to a pretrained floating point feature extractor, with a binary network. Additionally, we propose a feature similarity loss, a dynamic loss balancing and modified multi-stage training to further improve the accuracy, and call our method BURN. Our empirical validations over five downstream tasks using seven datasets show that BURN outperforms self-supervised baselines for binary networks and sometimes outperforms supervised pretraining. Code is availabe at https://github.com/naver-ai/burn.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2022 PDF CVPR 2022 Abstract