Self-Supervised Learning for Speech Enhancement through Synthesis
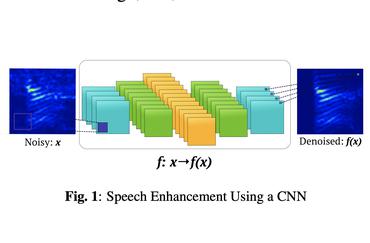
Modern speech enhancement (SE) networks typically implement noise suppression through time-frequency masking, latent representation masking, or discriminative signal prediction. In contrast, some recent works explore SE via generative speech synthesis, where the system's output is synthesized by a neural vocoder after an inherently lossy feature-denoising step. In this paper, we propose a denoising vocoder (DeVo) approach, where a vocoder accepts noisy representations and learns to directly synthesize clean speech. We leverage rich representations from self-supervised learning (SSL) speech models to discover relevant features. We conduct a candidate search across 15 potential SSL front-ends and subsequently train our vocoder adversarially with the best SSL configuration. Additionally, we demonstrate a causal version capable of running on streaming audio with 10ms latency and minimal performance degradation. Finally, we conduct both objective evaluations and subjective listening studies to show our system improves objective metrics and outperforms an existing state-of-the-art SE model subjectively.
PDF Abstract