Self-supervised Trajectory Representation Learning with Temporal Regularities and Travel Semantics
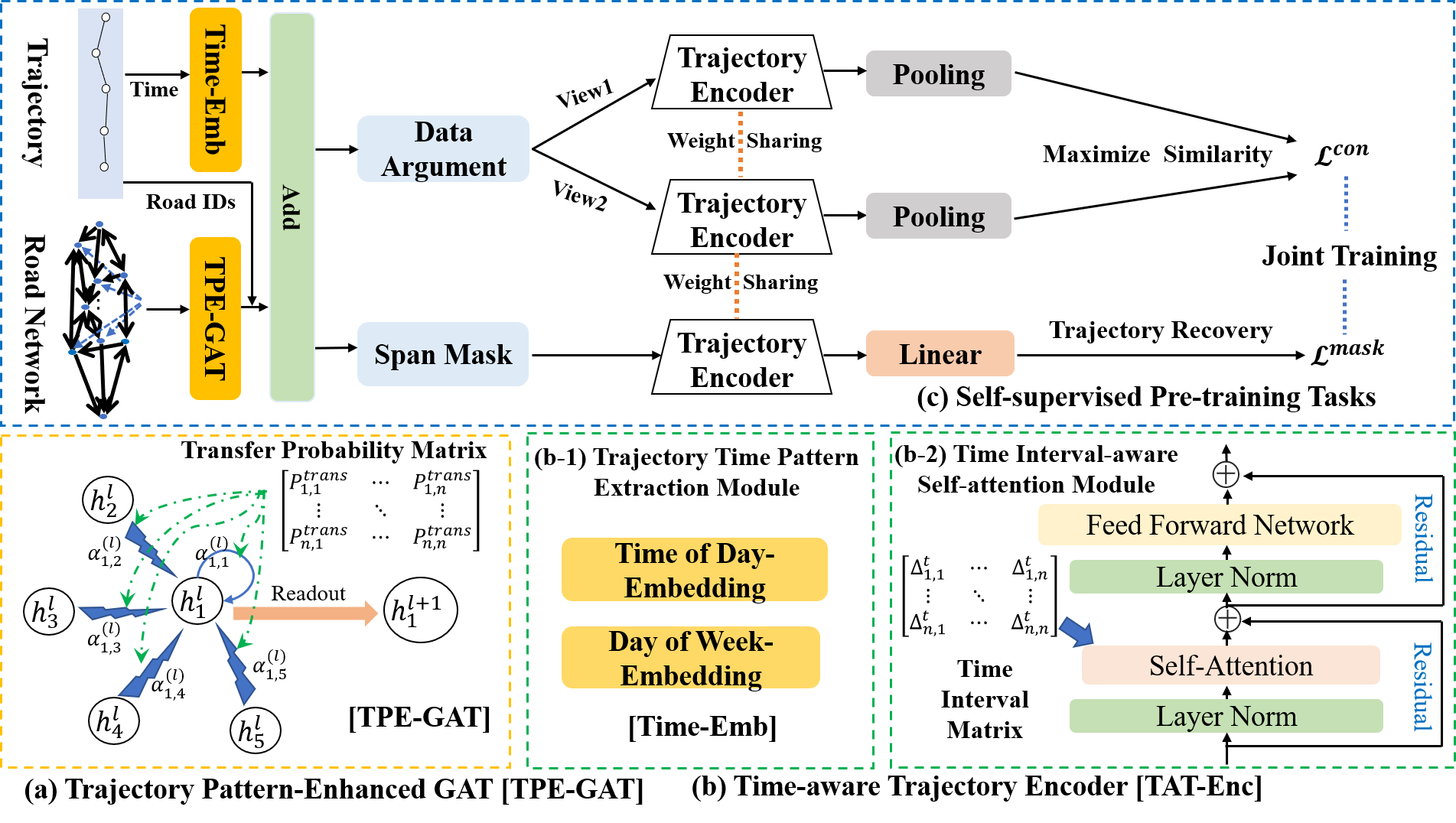
Trajectory Representation Learning (TRL) is a powerful tool for spatial-temporal data analysis and management. TRL aims to convert complicated raw trajectories into low-dimensional representation vectors, which can be applied to various downstream tasks, such as trajectory classification, clustering, and similarity computation. Existing TRL works usually treat trajectories as ordinary sequence data, while some important spatial-temporal characteristics, such as temporal regularities and travel semantics, are not fully exploited. To fill this gap, we propose a novel Self-supervised trajectory representation learning framework with TemporAl Regularities and Travel semantics, namely START. The proposed method consists of two stages. The first stage is a Trajectory Pattern-Enhanced Graph Attention Network (TPE-GAT), which converts the road network features and travel semantics into representation vectors of road segments. The second stage is a Time-Aware Trajectory Encoder (TAT-Enc), which encodes representation vectors of road segments in the same trajectory as a trajectory representation vector, meanwhile incorporating temporal regularities with the trajectory representation. Moreover, we also design two self-supervised tasks, i.e., span-masked trajectory recovery and trajectory contrastive learning, to introduce spatial-temporal characteristics of trajectories into the training process of our START framework. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by extensive experiments on two large-scale real-world datasets for three downstream tasks. The experiments also demonstrate that our method can be transferred across different cities to adapt heterogeneous trajectory datasets.
PDF Abstract