SNR-Based Features and Diverse Training Data for Robust DNN-Based Speech Enhancement
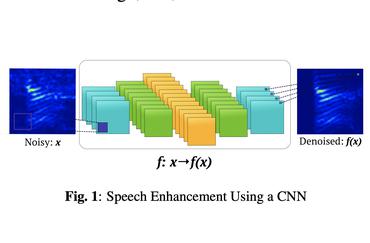
In this paper, we address the generalization of deep neural network (DNN) based speech enhancement to unseen noise conditions for the case that training data is limited in size and diversity. To gain more insights, we analyze the generalization with respect to (1) the size and diversity of the training data, (2) different network architectures, and (3) the chosen features. To address (1), we train networks on the Hu noise corpus (limited size), the CHiME 3 noise corpus (limited diversity) and also propose a large and diverse dataset collected based on freely available sounds. To address (2), we compare a fully-connected feed-forward and a long short-term memory (LSTM) architecture. To address (3), we compare three input features, namely logarithmized noisy periodograms, noise aware training (NAT) and the proposed signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) based noise aware training (SNR-NAT). We confirm that rich training data and improved network architectures help DNNs to generalize. Furthermore, we show via experimental results and an analysis using t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) that the proposed SNR-NAT features yield robust and level independent results in unseen noise even with simple network architectures and when trained on only small datasets, which is the key contribution of this paper.
PDF Abstract