Stepwise-Refining Speech Separation Network via Fine-Grained Encoding in High-order Latent Domain
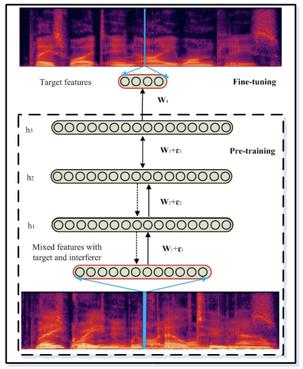
The crux of single-channel speech separation is how to encode the mixture of signals into such a latent embedding space that the signals from different speakers can be precisely separated. Existing methods for speech separation either transform the speech signals into frequency domain to perform separation or seek to learn a separable embedding space by constructing a latent domain based on convolutional filters. While the latter type of methods learning an embedding space achieves substantial improvement for speech separation, we argue that the embedding space defined by only one latent domain does not suffice to provide a thoroughly separable encoding space for speech separation. In this paper, we propose the Stepwise-Refining Speech Separation Network (SRSSN), which follows a coarse-to-fine separation framework. It first learns a 1-order latent domain to define an encoding space and thereby performs a rough separation in the coarse phase. Then the proposed SRSSN learns a new latent domain along each basis function of the existing latent domain to obtain a high-order latent domain in the refining phase, which enables our model to perform a refining separation to achieve a more precise speech separation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our SRSSN by conducting extensive experiments, including speech separation in a clean (noise-free) setting on WSJ0-2/3mix datasets as well as in noisy/reverberant settings on WHAM!/WHAMR! datasets. Furthermore, we also perform experiments of speech recognition on separated speech signals by our model to evaluate the performance of speech separation indirectly.
PDF Abstract



 WSJ0-2mix
WSJ0-2mix
