Async-HFL: Efficient and Robust Asynchronous Federated Learning in Hierarchical IoT Networks
Federated Learning (FL) has gained increasing interest in recent years as a distributed on-device learning paradigm. However, multiple challenges remain to be addressed for deploying FL in real-world Internet-of-Things (IoT) networks with hierarchies. Although existing works have proposed various approaches to account data heterogeneity, system heterogeneity, unexpected stragglers and scalibility, none of them provides a systematic solution to address all of the challenges in a hierarchical and unreliable IoT network. In this paper, we propose an asynchronous and hierarchical framework (Async-HFL) for performing FL in a common three-tier IoT network architecture. In response to the largely varied delays, Async-HFL employs asynchronous aggregations at both the gateway and the cloud levels thus avoids long waiting time. To fully unleash the potential of Async-HFL in converging speed under system heterogeneities and stragglers, we design device selection at the gateway level and device-gateway association at the cloud level. Device selection chooses edge devices to trigger local training in real-time while device-gateway association determines the network topology periodically after several cloud epochs, both satisfying bandwidth limitation. We evaluate Async-HFL's convergence speedup using large-scale simulations based on ns-3 and a network topology from NYCMesh. Our results show that Async-HFL converges 1.08-1.31x faster in wall-clock time and saves up to 21.6% total communication cost compared to state-of-the-art asynchronous FL algorithms (with client selection). We further validate Async-HFL on a physical deployment and observe robust convergence under unexpected stragglers.
PDF Abstract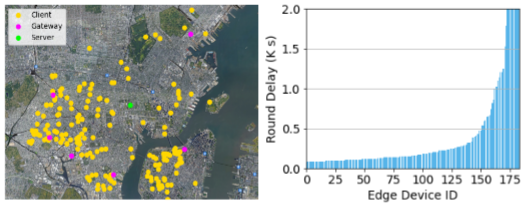


 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
 Fashion-MNIST
Fashion-MNIST
 HAR
HAR