Back to Optimization: Diffusion-based Zero-Shot 3D Human Pose Estimation
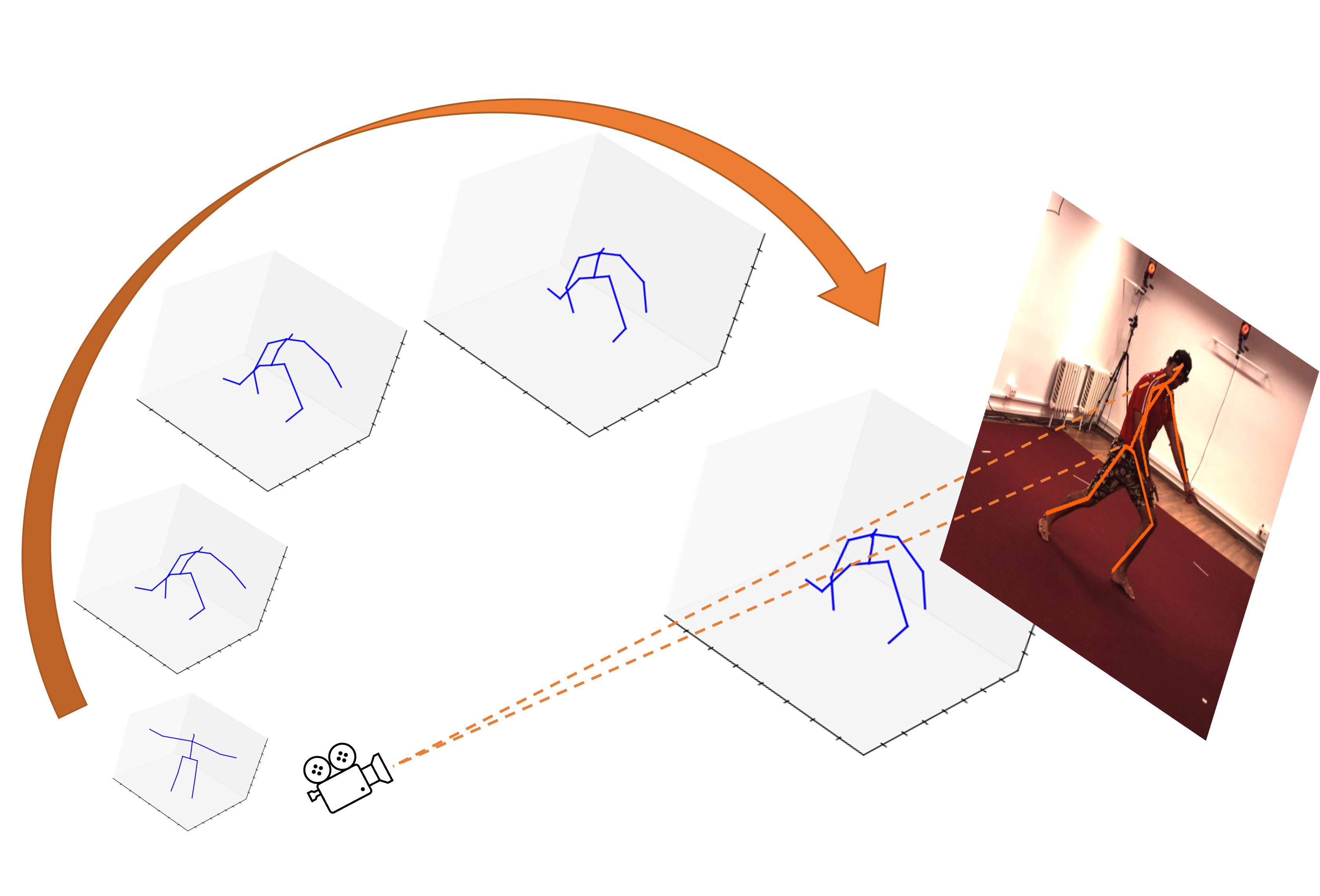
Learning-based methods have dominated the 3D human pose estimation (HPE) tasks with significantly better performance in most benchmarks than traditional optimization-based methods. Nonetheless, 3D HPE in the wild is still the biggest challenge for learning-based models, whether with 2D-3D lifting, image-to-3D, or diffusion-based methods, since the trained networks implicitly learn camera intrinsic parameters and domain-based 3D human pose distributions and estimate poses by statistical average. On the other hand, the optimization-based methods estimate results case-by-case, which can predict more diverse and sophisticated human poses in the wild. By combining the advantages of optimization-based and learning-based methods, we propose the \textbf{Ze}ro-shot \textbf{D}iffusion-based \textbf{O}ptimization (\textbf{ZeDO}) pipeline for 3D HPE to solve the problem of cross-domain and in-the-wild 3D HPE. Our multi-hypothesis \textit{\textbf{ZeDO}} achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on Human3.6M, with minMPJPE $51.4$mm, without training with any 2D-3D or image-3D pairs. Moreover, our single-hypothesis \textit{\textbf{ZeDO}} achieves SOTA performance on 3DPW dataset with PA-MPJPE $40.3$mm on cross-dataset evaluation, which even outperforms learning-based methods trained on 3DPW.
PDF AbstractDatasets
Results from the Paper
 Ranked #10 on
3D Human Pose Estimation
on 3DPW
(PA-MPJPE metric)
Ranked #10 on
3D Human Pose Estimation
on 3DPW
(PA-MPJPE metric)







 Human3.6M
Human3.6M
 3DPW
3DPW
 MPI-INF-3DHP
MPI-INF-3DHP
 Ski-Pose PTZ-Camera
Ski-Pose PTZ-Camera