Brain Anatomy Prior Modeling to Forecast Clinical Progression of Cognitive Impairment with Structural MRI
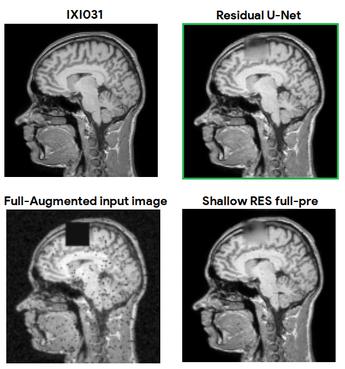
Brain structural MRI has been widely used to assess the future progression of cognitive impairment (CI). Previous learning-based studies usually suffer from the issue of small-sized labeled training data, while there exist a huge amount of structural MRIs in large-scale public databases. Intuitively, brain anatomical structures derived from these public MRIs (even without task-specific label information) can be used to boost CI progression trajectory prediction. However, previous studies seldom take advantage of such brain anatomy prior. To this end, this paper proposes a brain anatomy prior modeling (BAPM) framework to forecast the clinical progression of cognitive impairment with small-sized target MRIs by exploring anatomical brain structures. Specifically, the BAPM consists of a pretext model and a downstream model, with a shared brain anatomy-guided encoder to model brain anatomy prior explicitly. Besides the encoder, the pretext model also contains two decoders for two auxiliary tasks (i.e., MRI reconstruction and brain tissue segmentation), while the downstream model relies on a predictor for classification. The brain anatomy-guided encoder is pre-trained with the pretext model on 9,344 auxiliary MRIs without diagnostic labels for anatomy prior modeling. With this encoder frozen, the downstream model is then fine-tuned on limited target MRIs for prediction. We validate the BAPM on two CI-related studies with T1-weighted MRIs from 448 subjects. Experimental results suggest the effectiveness of BAPM in (1) four CI progression prediction tasks, (2) MR image reconstruction, and (3) brain tissue segmentation, compared with several state-of-the-art methods.
PDF Abstract