Deep Complex Networks
At present, the vast majority of building blocks, techniques, and architectures for deep learning are based on real-valued operations and representations. However, recent work on recurrent neural networks and older fundamental theoretical analysis suggests that complex numbers could have a richer representational capacity and could also facilitate noise-robust memory retrieval mechanisms. Despite their attractive properties and potential for opening up entirely new neural architectures, complex-valued deep neural networks have been marginalized due to the absence of the building blocks required to design such models. In this work, we provide the key atomic components for complex-valued deep neural networks and apply them to convolutional feed-forward networks and convolutional LSTMs. More precisely, we rely on complex convolutions and present algorithms for complex batch-normalization, complex weight initialization strategies for complex-valued neural nets and we use them in experiments with end-to-end training schemes. We demonstrate that such complex-valued models are competitive with their real-valued counterparts. We test deep complex models on several computer vision tasks, on music transcription using the MusicNet dataset and on Speech Spectrum Prediction using the TIMIT dataset. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on these audio-related tasks.
PDF Abstract ICLR 2018 PDF ICLR 2018 Abstract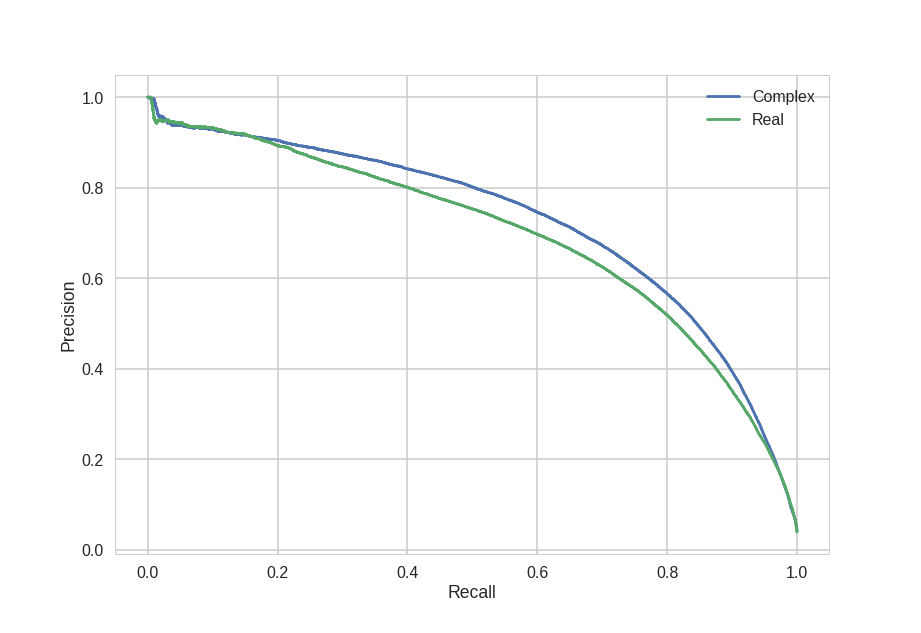







 CIFAR-10
CIFAR-10
 SVHN
SVHN
 MusicNet
MusicNet
