Discriminative Region Suppression for Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) using image-level labels has recently attracted much attention for reducing annotation costs. Existing WSSS methods utilize localization maps from the classification network to generate pseudo segmentation labels. However, since localization maps obtained from the classifier focus only on sparse discriminative object regions, it is difficult to generate high-quality segmentation labels. To address this issue, we introduce discriminative region suppression (DRS) module that is a simple yet effective method to expand object activation regions. DRS suppresses the attention on discriminative regions and spreads it to adjacent non-discriminative regions, generating dense localization maps. DRS requires few or no additional parameters and can be plugged into any network. Furthermore, we introduce an additional learning strategy to give a self-enhancement of localization maps, named localization map refinement learning. Benefiting from this refinement learning, localization maps are refined and enhanced by recovering some missing parts or removing noise itself. Due to its simplicity and effectiveness, our approach achieves mIoU 71.4% on the PASCAL VOC 2012 segmentation benchmark using only image-level labels. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. The code is available at https://github.com/qjadud1994/DRS.
PDF Abstract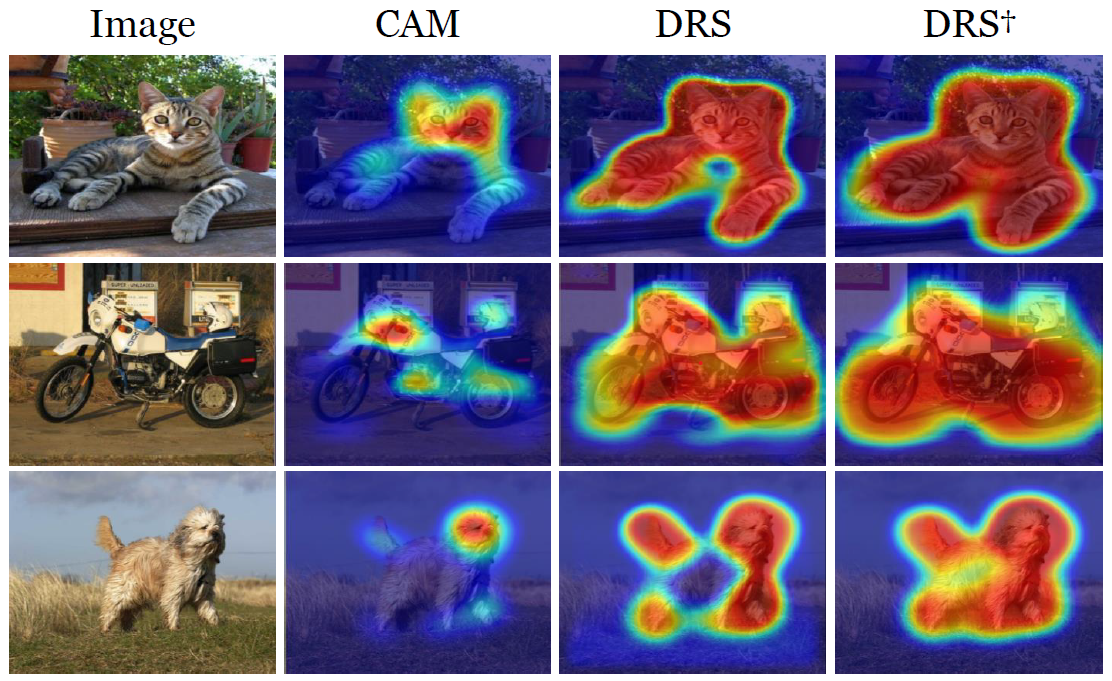






 VOC 2012
VOC 2012
