Distilled Wasserstein Learning for Word Embedding and Topic Modeling
We propose a novel Wasserstein method with a distillation mechanism, yielding joint learning of word embeddings and topics. The proposed method is based on the fact that the Euclidean distance between word embeddings may be employed as the underlying distance in the Wasserstein topic model. The word distributions of topics, their optimal transports to the word distributions of documents, and the embeddings of words are learned in a unified framework. When learning the topic model, we leverage a distilled underlying distance matrix to update the topic distributions and smoothly calculate the corresponding optimal transports. Such a strategy provides the updating of word embeddings with robust guidance, improving the algorithmic convergence. As an application, we focus on patient admission records, in which the proposed method embeds the codes of diseases and procedures and learns the topics of admissions, obtaining superior performance on clinically-meaningful disease network construction, mortality prediction as a function of admission codes, and procedure recommendation.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2018 PDF NeurIPS 2018 Abstract
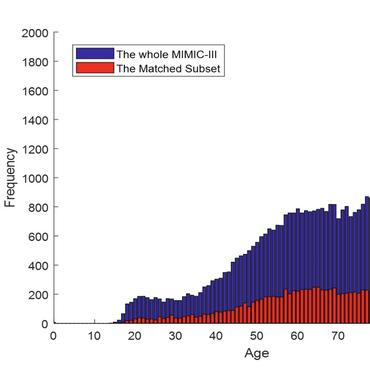

 MIMIC-III
MIMIC-III