Diverse Image-to-Image Translation via Disentangled Representations
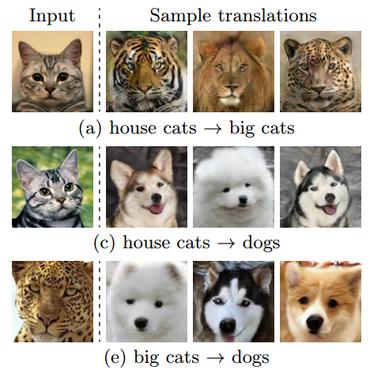
Image-to-image translation aims to learn the mapping between two visual domains. There are two main challenges for many applications: 1) the lack of aligned training pairs and 2) multiple possible outputs from a single input image. In this work, we present an approach based on disentangled representation for producing diverse outputs without paired training images. To achieve diversity, we propose to embed images onto two spaces: a domain-invariant content space capturing shared information across domains and a domain-specific attribute space. Our model takes the encoded content features extracted from a given input and the attribute vectors sampled from the attribute space to produce diverse outputs at test time. To handle unpaired training data, we introduce a novel cross-cycle consistency loss based on disentangled representations. Qualitative results show that our model can generate diverse and realistic images on a wide range of tasks without paired training data. For quantitative comparisons, we measure realism with user study and diversity with a perceptual distance metric. We apply the proposed model to domain adaptation and show competitive performance when compared to the state-of-the-art on the MNIST-M and the LineMod datasets.
PDF Abstract ECCV 2018 PDF ECCV 2018 Abstract








 MNIST
MNIST
 CelebA-HQ
CelebA-HQ
 GTA5
GTA5
 AFHQ
AFHQ
 MNIST-M
MNIST-M
