Few-Shot Specific Emitter Identification via Deep Metric Ensemble Learning
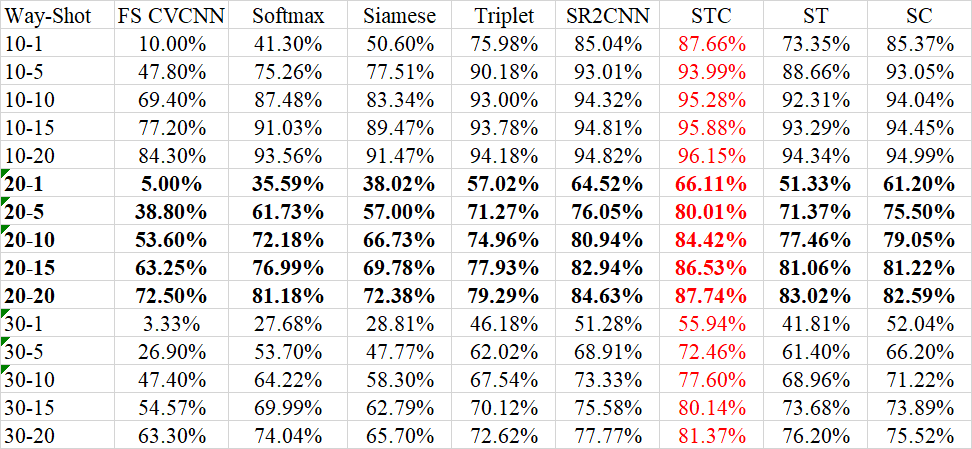
Specific emitter identification (SEI) is a highly potential technology for physical layer authentication that is one of the most critical supplement for the upper-layer authentication. SEI is based on radio frequency (RF) features from circuit difference, rather than cryptography. These features are inherent characteristic of hardware circuits, which difficult to counterfeit. Recently, various deep learning (DL)-based conventional SEI methods have been proposed, and achieved advanced performances. However, these methods are proposed for close-set scenarios with massive RF signal samples for training, and they generally have poor performance under the condition of limited training samples. Thus, we focus on few-shot SEI (FS-SEI) for aircraft identification via automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast (ADS-B) signals, and a novel FS-SEI method is proposed, based on deep metric ensemble learning (DMEL). Specifically, the proposed method consists of feature embedding and classification. The former is based on metric learning with complex-valued convolutional neural network (CVCNN) for extracting discriminative features with compact intra-category distance and separable inter-category distance, while the latter is realized by an ensemble classifier. Simulation results show that if the number of samples per category is more than 5, the average accuracy of our proposed method is higher than 98\%. Moreover, feature visualization demonstrates the advantages of our proposed method in both discriminability and generalization. The codes of this paper can be downloaded from GitHub(https://github.com/BeechburgPieStar/Few-Shot-Specific-Emitter-Identification-via-Deep-Metric-Ensemble-Learning)
PDF Abstract