Lifelong Person Re-Identification via Adaptive Knowledge Accumulation
Person ReID methods always learn through a stationary domain that is fixed by the choice of a given dataset. In many contexts (e.g., lifelong learning), those methods are ineffective because the domain is continually changing in which case incremental learning over multiple domains is required potentially. In this work we explore a new and challenging ReID task, namely lifelong person re-identification (LReID), which enables to learn continuously across multiple domains and even generalise on new and unseen domains. Following the cognitive processes in the human brain, we design an Adaptive Knowledge Accumulation (AKA) framework that is endowed with two crucial abilities: knowledge representation and knowledge operation. Our method alleviates catastrophic forgetting on seen domains and demonstrates the ability to generalize to unseen domains. Correspondingly, we also provide a new and large-scale benchmark for LReID. Extensive experiments demonstrate our method outperforms other competitors by a margin of 5.8% mAP in generalising evaluation.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2021 PDF CVPR 2021 Abstract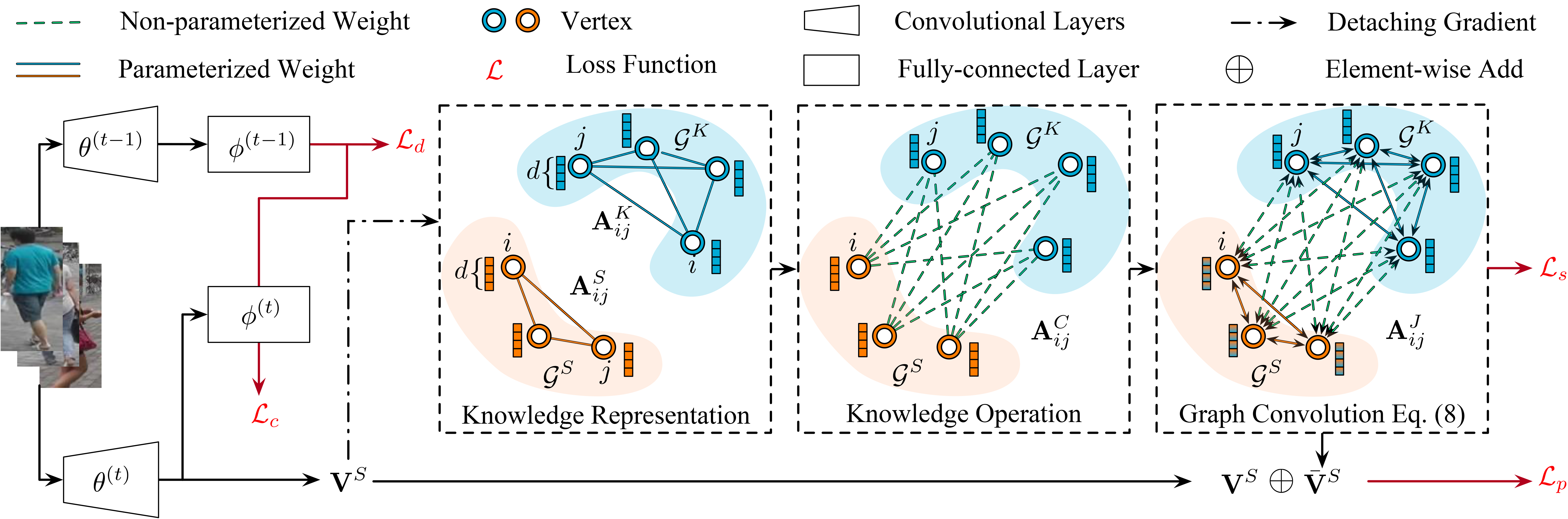



 CIFAR-100
CIFAR-100