MGTANet: Encoding Sequential LiDAR Points Using Long Short-Term Motion-Guided Temporal Attention for 3D Object Detection
Most scanning LiDAR sensors generate a sequence of point clouds in real-time. While conventional 3D object detectors use a set of unordered LiDAR points acquired over a fixed time interval, recent studies have revealed that substantial performance improvement can be achieved by exploiting the spatio-temporal context present in a sequence of LiDAR point sets. In this paper, we propose a novel 3D object detection architecture, which can encode LiDAR point cloud sequences acquired by multiple successive scans. The encoding process of the point cloud sequence is performed on two different time scales. We first design a short-term motion-aware voxel encoding that captures the short-term temporal changes of point clouds driven by the motion of objects in each voxel. We also propose long-term motion-guided bird's eye view (BEV) feature enhancement that adaptively aligns and aggregates the BEV feature maps obtained by the short-term voxel encoding by utilizing the dynamic motion context inferred from the sequence of the feature maps. The experiments conducted on the public nuScenes benchmark demonstrate that the proposed 3D object detector offers significant improvements in performance compared to the baseline methods and that it sets a state-of-the-art performance for certain 3D object detection categories. Code is available at https://github.com/HYjhkoh/MGTANet.git
PDF Abstract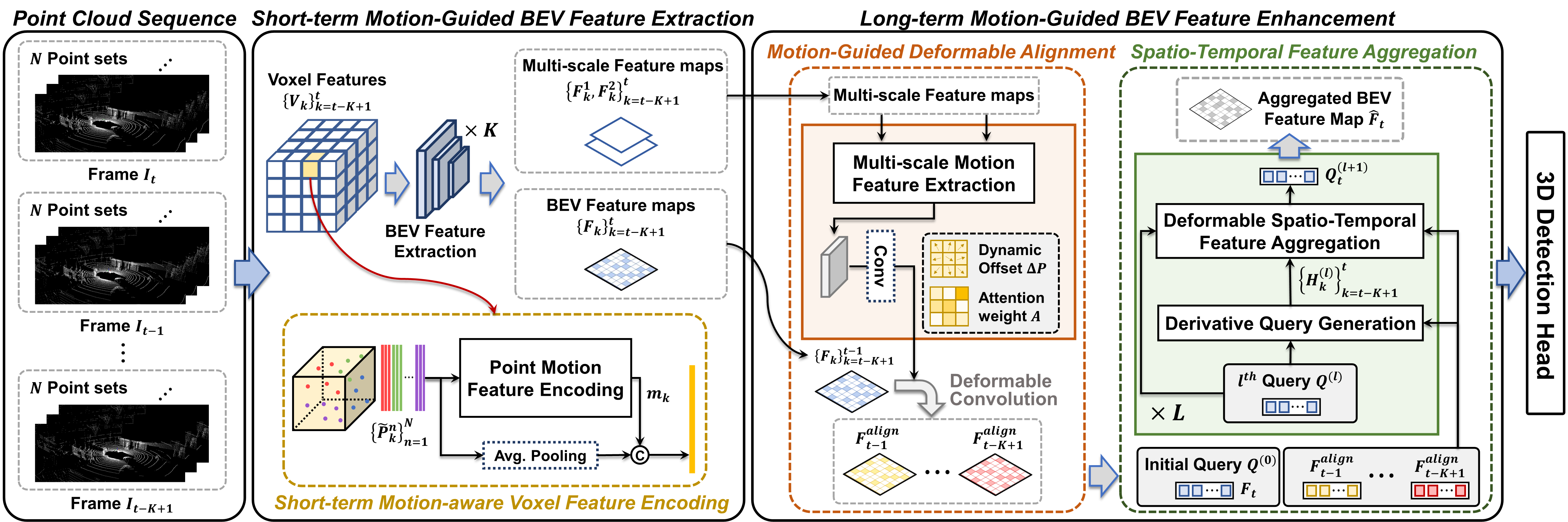





 nuScenes
nuScenes
