MSFlow: Multi-Scale Flow-based Framework for Unsupervised Anomaly Detection
Unsupervised anomaly detection (UAD) attracts a lot of research interest and drives widespread applications, where only anomaly-free samples are available for training. Some UAD applications intend to further locate the anomalous regions without any anomaly information. Although the absence of anomalous samples and annotations deteriorates the UAD performance, an inconspicuous yet powerful statistics model, the normalizing flows, is appropriate for anomaly detection and localization in an unsupervised fashion. The flow-based probabilistic models, only trained on anomaly-free data, can efficiently distinguish unpredictable anomalies by assigning them much lower likelihoods than normal data. Nevertheless, the size variation of unpredictable anomalies introduces another inconvenience to the flow-based methods for high-precision anomaly detection and localization. To generalize the anomaly size variation, we propose a novel Multi-Scale Flow-based framework dubbed MSFlow composed of asymmetrical parallel flows followed by a fusion flow to exchange multi-scale perceptions. Moreover, different multi-scale aggregation strategies are adopted for image-wise anomaly detection and pixel-wise anomaly localization according to the discrepancy between them. The proposed MSFlow is evaluated on three anomaly detection datasets, significantly outperforming existing methods. Notably, on the challenging MVTec AD benchmark, our MSFlow achieves a new state-of-the-art with a detection AUORC score of up to 99.7%, localization AUCROC score of 98.8%, and PRO score of 97.1%. The reproducible code is available at https://github.com/cool-xuan/msflow.
PDF Abstract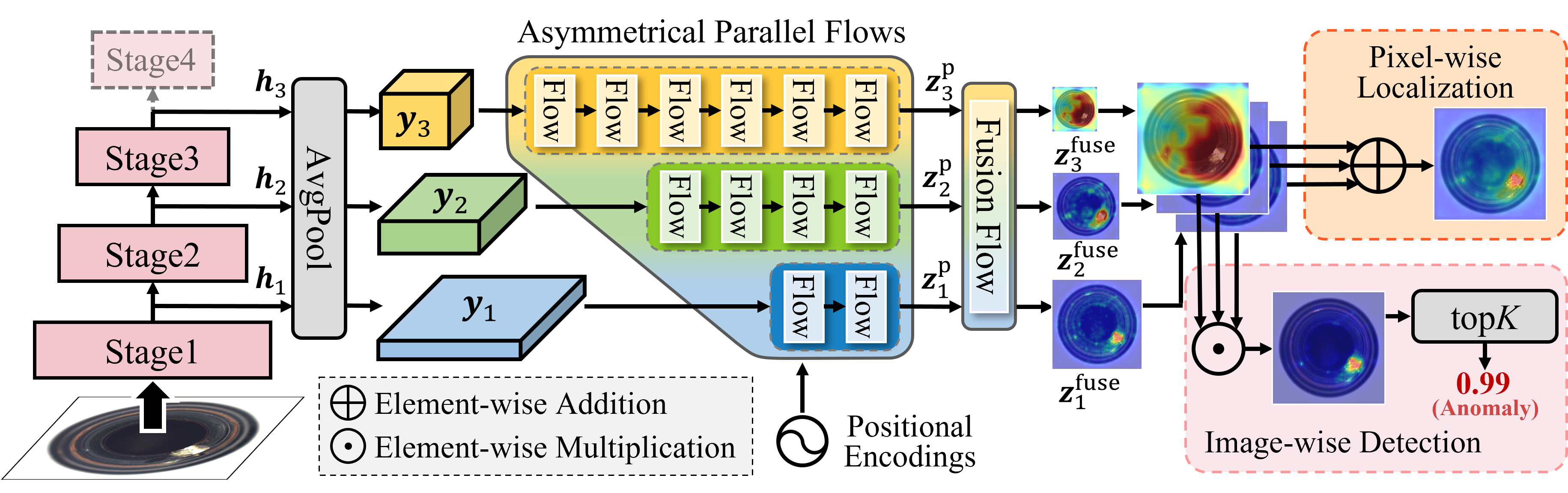




 MVTecAD
MVTecAD
