PEPSI: Pathology-Enhanced Pulse-Sequence-Invariant Representations for Brain MRI
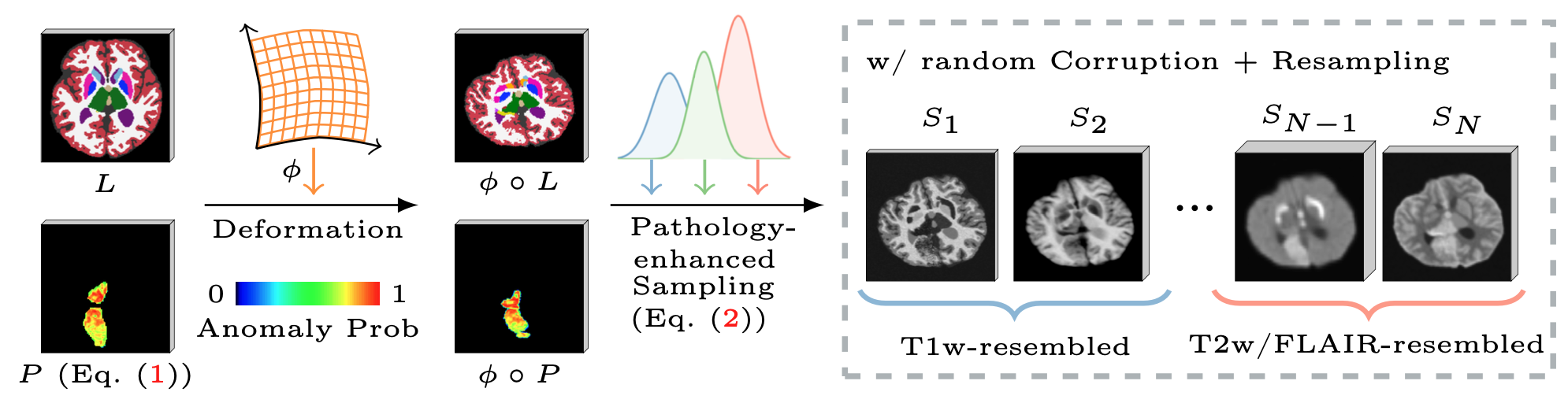
Remarkable progress has been made by data-driven machine-learning methods in the analysis of MRI scans. However, most existing MRI analysis approaches are crafted for specific MR pulse sequences (MR contrasts) and usually require nearly isotropic acquisitions. This limits their applicability to diverse real-world clinical data, where scans commonly exhibit variations in appearances due to being obtained with varying sequence parameters, resolutions, and orientations -- especially in the presence of pathology. In this paper, we propose PEPSI, the first pathology-enhanced, and pulse-sequence-invariant feature representation learning model for brain MRI. PEPSI is trained entirely on synthetic images with a novel pathology encoding strategy, and enables co-training across datasets with diverse pathologies and missing modalities. Despite variations in pathology appearances across different MR pulse sequences or the quality of acquired images (e.g., resolution, orientation, artifacts, etc), PEPSI produces a high-resolution image of reference contrast (MP-RAGE) that captures anatomy, along with an image specifically highlighting the pathology. Our experiments demonstrate PEPSI's remarkable capability for image synthesis compared with the state-of-the-art, contrast-agnostic synthesis models, as it accurately reconstructs anatomical structures while differentiating between pathology and normal tissue. We further illustrate the efficiency and effectiveness of PEPSI features for downstream pathology segmentations on five public datasets covering white matter hyperintensities and stroke lesions. Code is available at https://github.com/peirong26/PEPSI.
PDF Abstract