Wasserstein Random Forests and Applications in Heterogeneous Treatment Effects
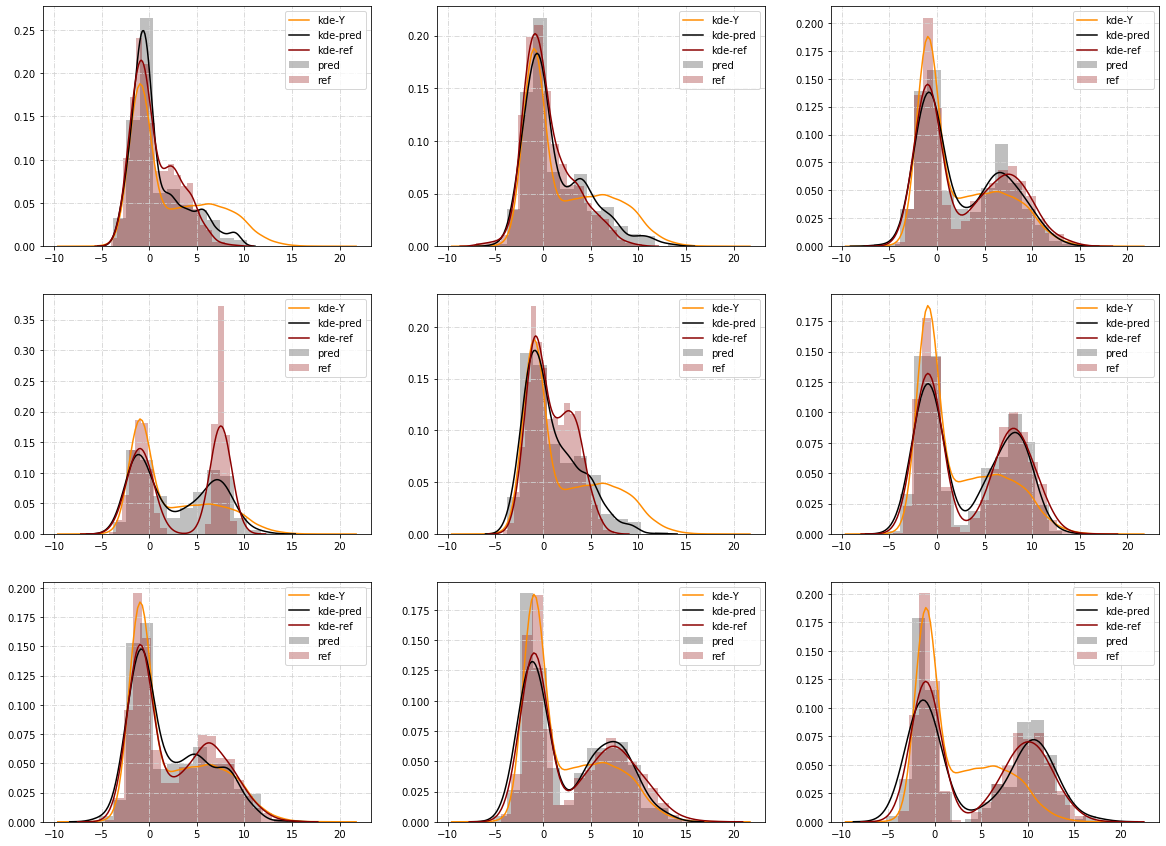
We present new insights into causal inference in the context of Heterogeneous Treatment Effects by proposing natural variants of Random Forests to estimate the key conditional distributions. To achieve this, we recast Breiman's original splitting criterion in terms of Wasserstein distances between empirical measures. This reformulation indicates that Random Forests are well adapted to estimate conditional distributions and provides a natural extension of the algorithm to multivariate outputs. Following the philosophy of Breiman's construction, we propose some variants of the splitting rule that are well-suited to the conditional distribution estimation problem. Some preliminary theoretical connections are established along with various numerical experiments, which show how our approach may help to conduct more transparent causal inference in complex situations.
PDF Abstract