ConDA: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for LiDAR Segmentation via Regularized Domain Concatenation
Transferring knowledge learned from the labeled source domain to the raw target domain for unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) is essential to the scalable deployment of autonomous driving systems. State-of-the-art methods in UDA often employ a key idea: utilizing joint supervision signals from both source and target domains for self-training. In this work, we improve and extend this aspect. We present ConDA, a concatenation-based domain adaptation framework for LiDAR segmentation that: 1) constructs an intermediate domain consisting of fine-grained interchange signals from both source and target domains without destabilizing the semantic coherency of objects and background around the ego-vehicle; and 2) utilizes the intermediate domain for self-training. To improve the network training on the source domain and self-training on the intermediate domain, we propose an anti-aliasing regularizer and an entropy aggregator to reduce the negative effect caused by the aliasing artifacts and noisy pseudo labels. Through extensive studies, we demonstrate that ConDA significantly outperforms prior arts in mitigating domain gaps.
PDF Abstract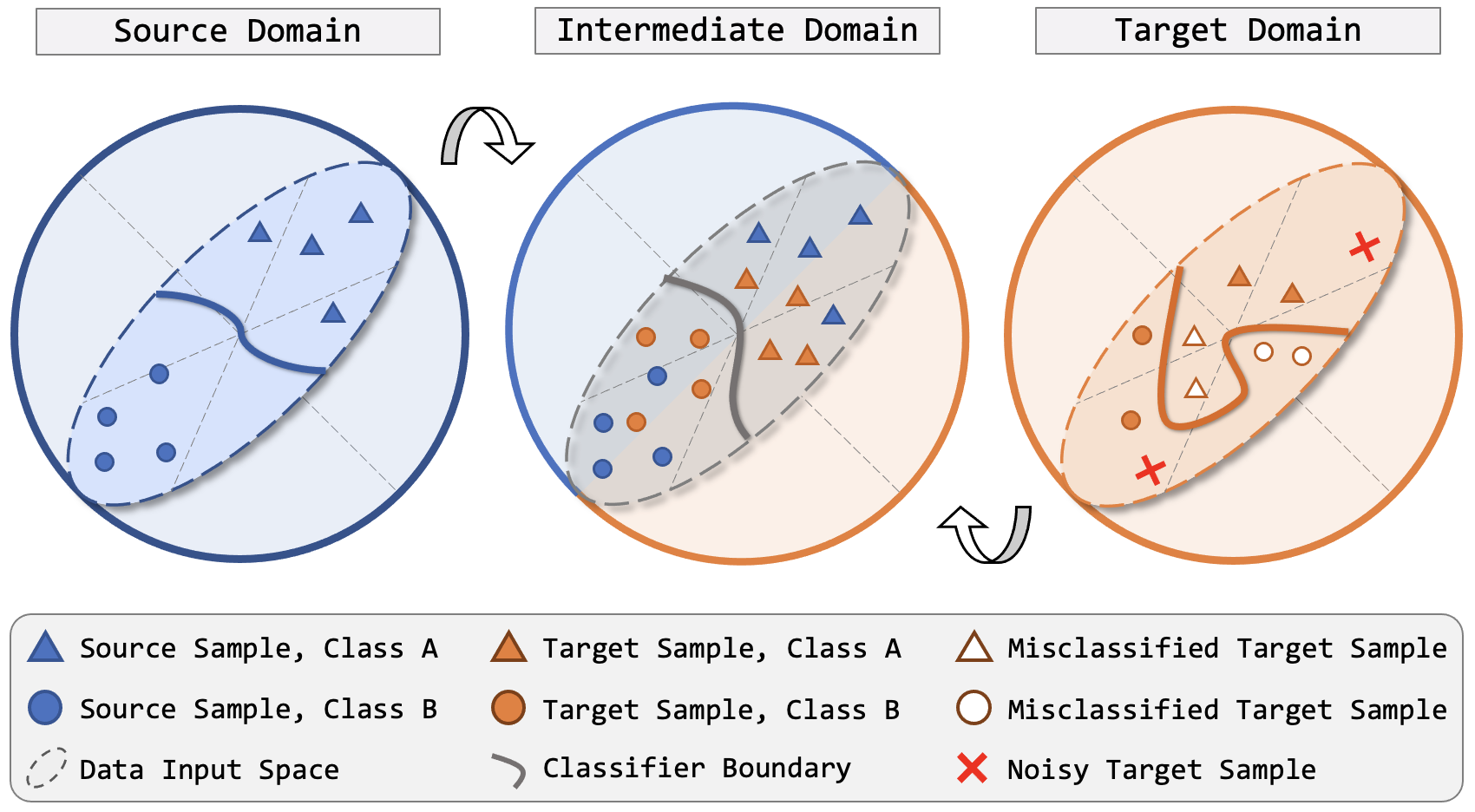





 nuScenes (Cross-City UDA)
nuScenes (Cross-City UDA)
 nuScenes
nuScenes