FlexiViT: One Model for All Patch Sizes
Vision Transformers convert images to sequences by slicing them into patches. The size of these patches controls a speed/accuracy tradeoff, with smaller patches leading to higher accuracy at greater computational cost, but changing the patch size typically requires retraining the model. In this paper, we demonstrate that simply randomizing the patch size at training time leads to a single set of weights that performs well across a wide range of patch sizes, making it possible to tailor the model to different compute budgets at deployment time. We extensively evaluate the resulting model, which we call FlexiViT, on a wide range of tasks, including classification, image-text retrieval, open-world detection, panoptic segmentation, and semantic segmentation, concluding that it usually matches, and sometimes outperforms, standard ViT models trained at a single patch size in an otherwise identical setup. Hence, FlexiViT training is a simple drop-in improvement for ViT that makes it easy to add compute-adaptive capabilities to most models relying on a ViT backbone architecture. Code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/google-research/big_vision
PDF Abstract CVPR 2023 PDF CVPR 2023 Abstract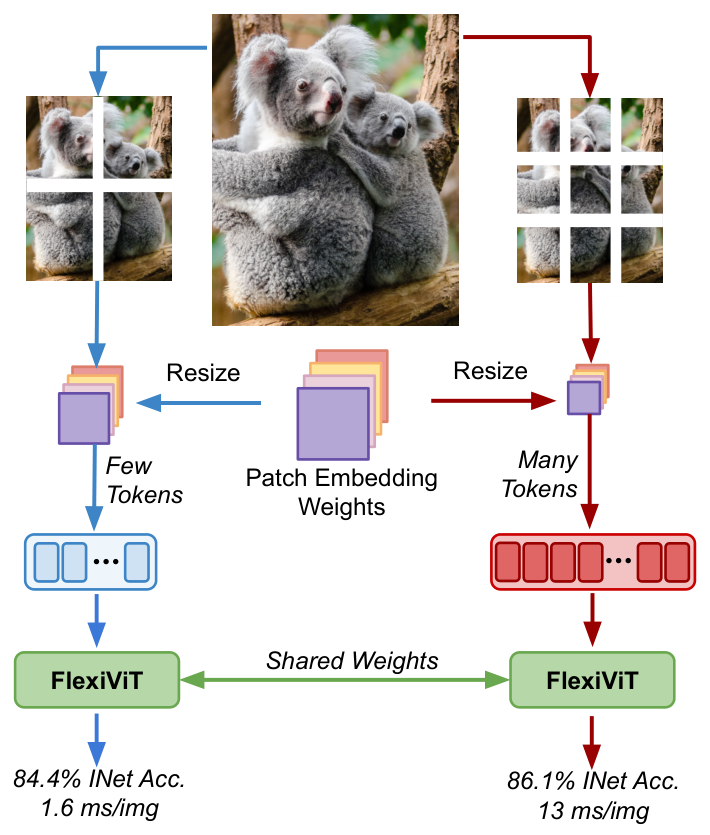





 MS COCO
MS COCO
 LVIS
LVIS