HDL: Hybrid Deep Learning for the Synthesis of Myocardial Velocity Maps in Digital Twins for Cardiac Analysis
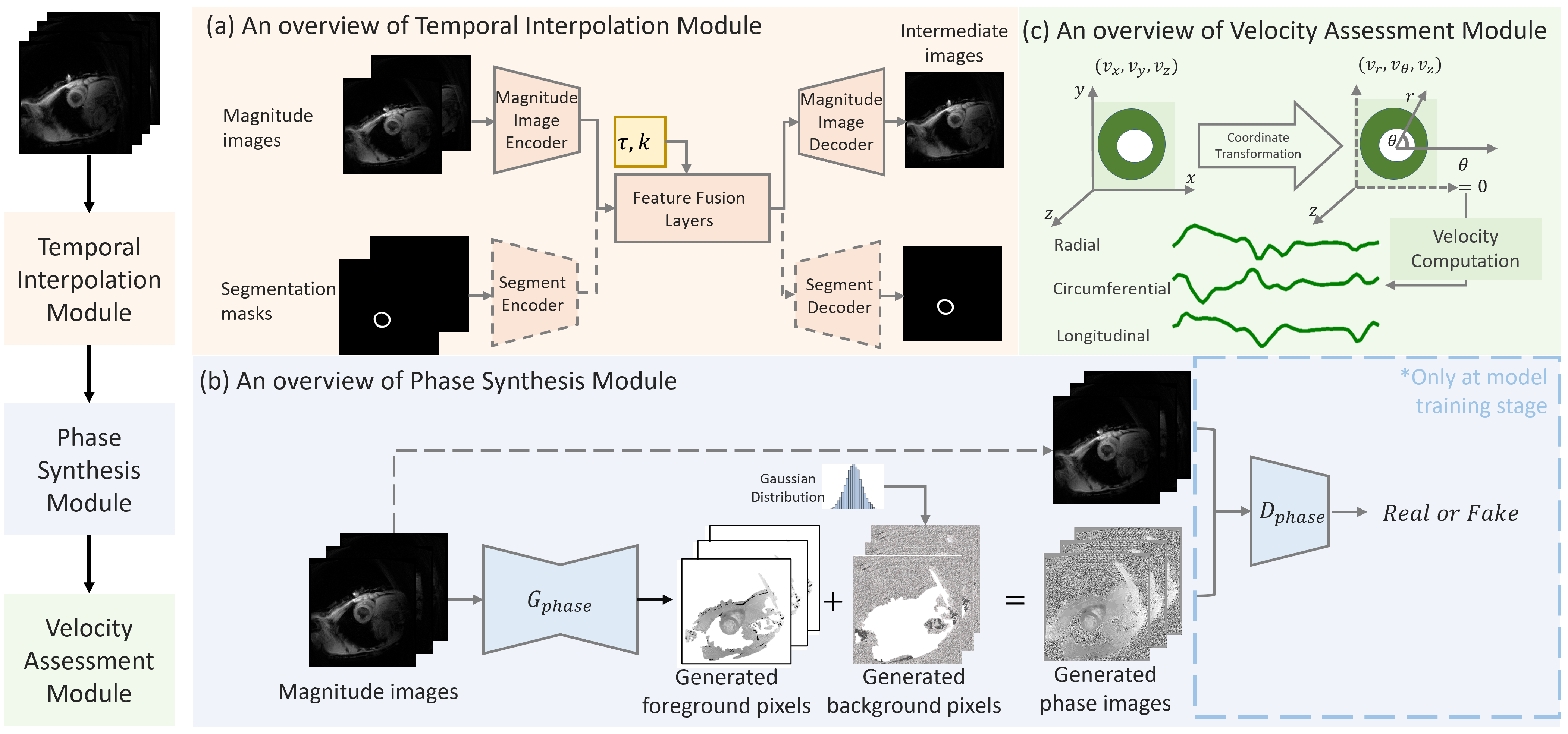
Synthetic digital twins based on medical data accelerate the acquisition, labelling and decision making procedure in digital healthcare. A core part of digital healthcare twins is model-based data synthesis, which permits the generation of realistic medical signals without requiring to cope with the modelling complexity of anatomical and biochemical phenomena producing them in reality. Unfortunately, algorithms for cardiac data synthesis have been so far scarcely studied in the literature. An important imaging modality in the cardiac examination is three-directional CINE multi-slice myocardial velocity mapping (3Dir MVM), which provides a quantitative assessment of cardiac motion in three orthogonal directions of the left ventricle. The long acquisition time and complex acquisition produce make it more urgent to produce synthetic digital twins of this imaging modality. In this study, we propose a hybrid deep learning (HDL) network, especially for synthetic 3Dir MVM data. Our algorithm is featured by a hybrid UNet and a Generative Adversarial Network with a foreground-background generation scheme. The experimental results show that from temporally down-sampled magnitude CINE images (six times), our proposed algorithm can still successfully synthesise high temporal resolution 3Dir MVM CMR data (PSNR=42.32) with precise left ventricle segmentation (DICE=0.92). These performance scores indicate that our proposed HDL algorithm can be implemented in real-world digital twins for myocardial velocity mapping data simulation. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first one in the literature investigating digital twins of the 3Dir MVM CMR, which has shown great potential for improving the efficiency of clinical studies via synthesised cardiac data.
PDF Abstract