Improved anomaly detection by training an autoencoder with skip connections on images corrupted with Stain-shaped noise
In industrial vision, the anomaly detection problem can be addressed with an autoencoder trained to map an arbitrary image, i.e. with or without any defect, to a clean image, i.e. without any defect. In this approach, anomaly detection relies conventionally on the reconstruction residual or, alternatively, on the reconstruction uncertainty. To improve the sharpness of the reconstruction, we consider an autoencoder architecture with skip connections. In the common scenario where only clean images are available for training, we propose to corrupt them with a synthetic noise model to prevent the convergence of the network towards the identity mapping, and introduce an original Stain noise model for that purpose. We show that this model favors the reconstruction of clean images from arbitrary real-world images, regardless of the actual defects appearance. In addition to demonstrating the relevance of our approach, our validation provides the first consistent assessment of reconstruction-based methods, by comparing their performance over the MVTec AD dataset, both for pixel- and image-wise anomaly detection.
PDF Abstract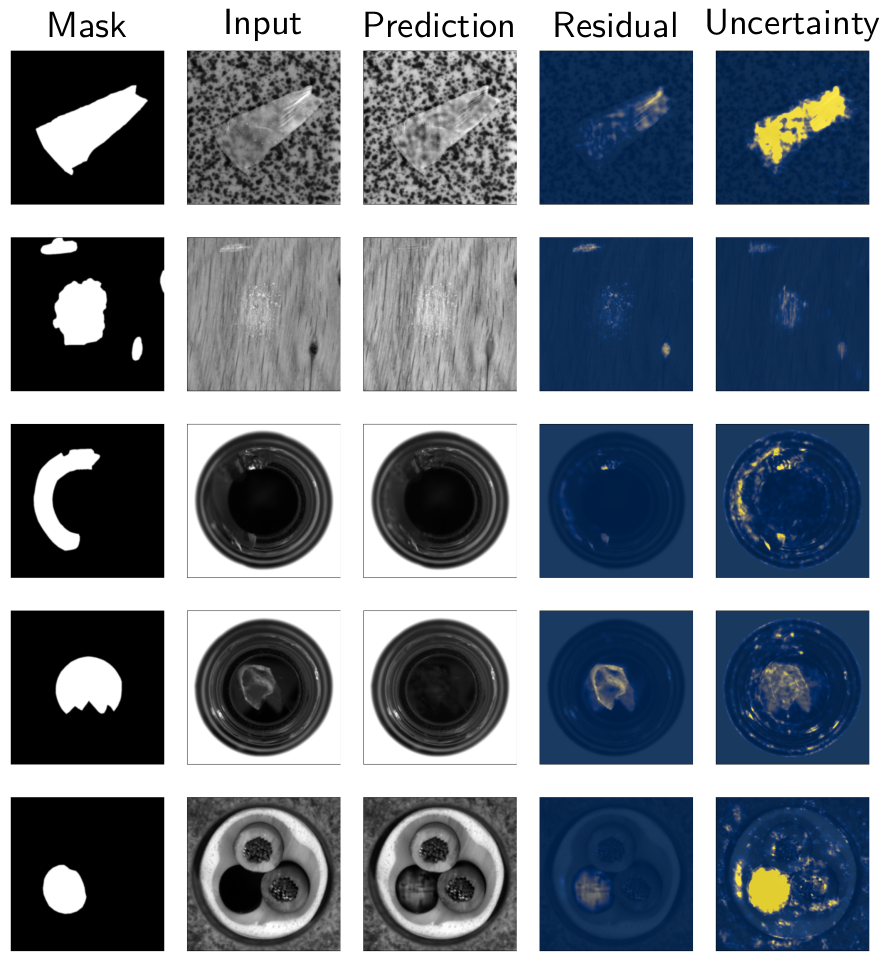

 MVTecAD
MVTecAD