Multi-Anchor Active Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation
Unsupervised domain adaption has proven to be an effective approach for alleviating the intensive workload of manual annotation by aligning the synthetic source-domain data and the real-world target-domain samples. Unfortunately, mapping the target-domain distribution to the source-domain unconditionally may distort the essential structural information of the target-domain data. To this end, we firstly propose to introduce a novel multi-anchor based active learning strategy to assist domain adaptation regarding the semantic segmentation task. By innovatively adopting multiple anchors instead of a single centroid, the source domain can be better characterized as a multimodal distribution, thus more representative and complimentary samples are selected from the target domain. With little workload to manually annotate these active samples, the distortion of the target-domain distribution can be effectively alleviated, resulting in a large performance gain. The multi-anchor strategy is additionally employed to model the target-distribution. By regularizing the latent representation of the target samples compact around multiple anchors through a novel soft alignment loss, more precise segmentation can be achieved. Extensive experiments are conducted on public datasets to demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods significantly, along with thorough ablation study to verify the effectiveness of each component.
PDF Abstract ICCV 2021 PDF ICCV 2021 Abstract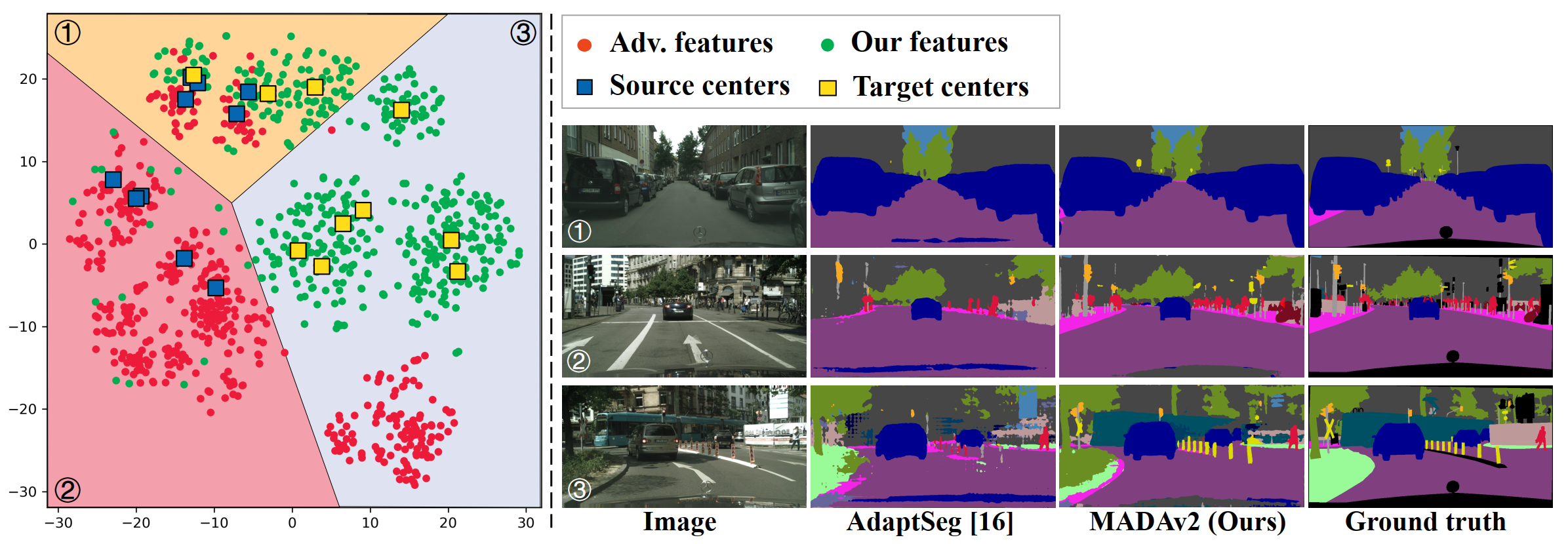




 Cityscapes
Cityscapes
 SYNTHIA
SYNTHIA
 GTA5
GTA5