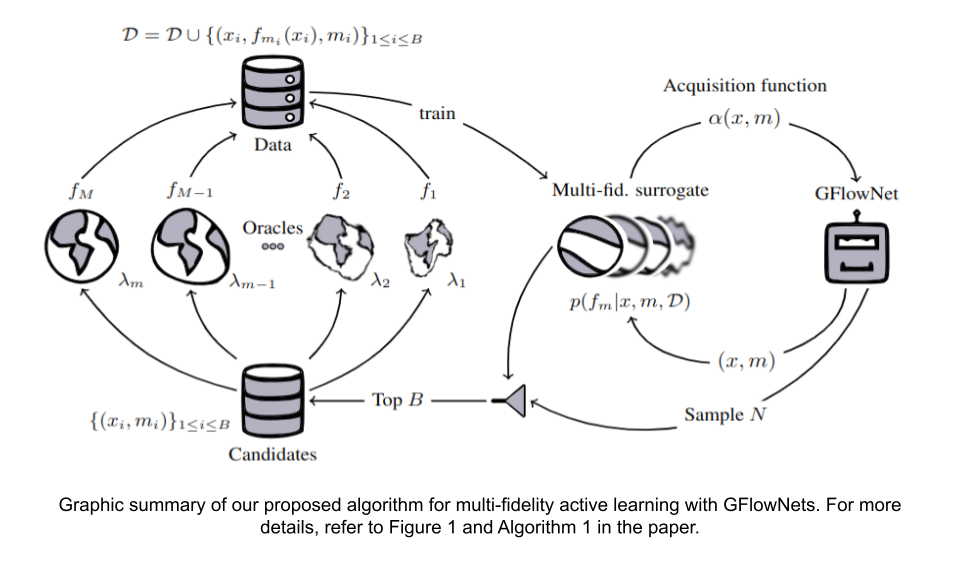
Multi-Fidelity Active Learning with GFlowNets
In the last decades, the capacity to generate large amounts of data in science and engineering applications has been growing steadily. Meanwhile, the progress in machine learning has turned it into a suitable tool to process and utilise the available data. Nonetheless, many relevant scientific and engineering problems present challenges where current machine learning methods cannot yet efficiently leverage the available data and resources. For example, in scientific discovery, we are often faced with the problem of exploring very large, high-dimensional spaces, where querying a high fidelity, black-box objective function is very expensive. Progress in machine learning methods that can efficiently tackle such problems would help accelerate currently crucial areas such as drug and materials discovery. In this paper, we propose the use of GFlowNets for multi-fidelity active learning, where multiple approximations of the black-box function are available at lower fidelity and cost. GFlowNets are recently proposed methods for amortised probabilistic inference that have proven efficient for exploring large, high-dimensional spaces and can hence be practical in the multi-fidelity setting too. Here, we describe our algorithm for multi-fidelity active learning with GFlowNets and evaluate its performance in both well-studied synthetic tasks and practically relevant applications of molecular discovery. Our results show that multi-fidelity active learning with GFlowNets can efficiently leverage the availability of multiple oracles with different costs and fidelities to accelerate scientific discovery and engineering design.
PDF Abstract