Pixel-wise Anomaly Detection in Complex Driving Scenes
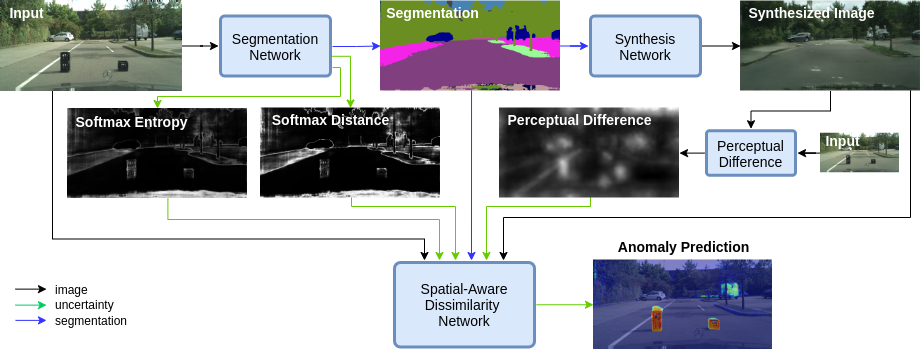
The inability of state-of-the-art semantic segmentation methods to detect anomaly instances hinders them from being deployed in safety-critical and complex applications, such as autonomous driving. Recent approaches have focused on either leveraging segmentation uncertainty to identify anomalous areas or re-synthesizing the image from the semantic label map to find dissimilarities with the input image. In this work, we demonstrate that these two methodologies contain complementary information and can be combined to produce robust predictions for anomaly segmentation. We present a pixel-wise anomaly detection framework that uses uncertainty maps to improve over existing re-synthesis methods in finding dissimilarities between the input and generated images. Our approach works as a general framework around already trained segmentation networks, which ensures anomaly detection without compromising segmentation accuracy, while significantly outperforming all similar methods. Top-2 performance across a range of different anomaly datasets shows the robustness of our approach to handling different anomaly instances.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2021 PDF CVPR 2021 AbstractCode
Datasets
Results from the Paper
 Ranked #3 on
Anomaly Detection
on Lost and Found
(using extra training data)
Ranked #3 on
Anomaly Detection
on Lost and Found
(using extra training data)





 Cityscapes
Cityscapes
 Lost and Found
Lost and Found
 Fishyscapes
Fishyscapes