Robust and Decomposable Average Precision for Image Retrieval
In image retrieval, standard evaluation metrics rely on score ranking, e.g. average precision (AP). In this paper, we introduce a method for robust and decomposable average precision (ROADMAP) addressing two major challenges for end-to-end training of deep neural networks with AP: non-differentiability and non-decomposability. Firstly, we propose a new differentiable approximation of the rank function, which provides an upper bound of the AP loss and ensures robust training. Secondly, we design a simple yet effective loss function to reduce the decomposability gap between the AP in the whole training set and its averaged batch approximation, for which we provide theoretical guarantees. Extensive experiments conducted on three image retrieval datasets show that ROADMAP outperforms several recent AP approximation methods and highlight the importance of our two contributions. Finally, using ROADMAP for training deep models yields very good performances, outperforming state-of-the-art results on the three datasets.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2021 PDF NeurIPS 2021 Abstract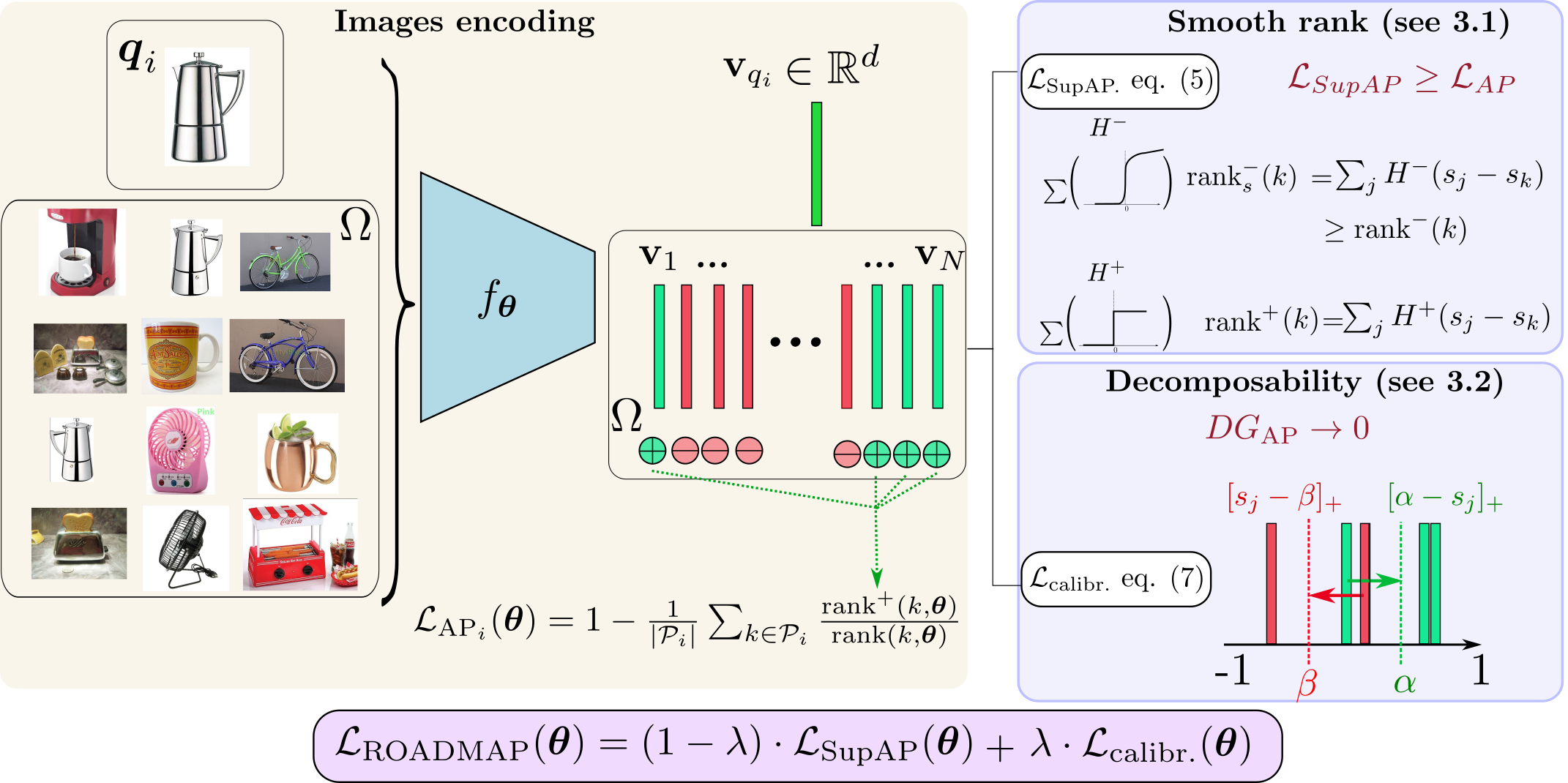








 CUB-200-2011
CUB-200-2011
 iNaturalist
iNaturalist
 Stanford Online Products
Stanford Online Products
