Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation: Solving the Edge-Fattening Problem
Self-supervised monocular depth estimation (MDE) models universally suffer from the notorious edge-fattening issue. Triplet loss, as a widespread metric learning strategy, has largely succeeded in many computer vision applications. In this paper, we redesign the patch-based triplet loss in MDE to alleviate the ubiquitous edge-fattening issue. We show two drawbacks of the raw triplet loss in MDE and demonstrate our problem-driven redesigns. First, we present a min. operator based strategy applied to all negative samples, to prevent well-performing negatives sheltering the error of edge-fattening negatives. Second, we split the anchor-positive distance and anchor-negative distance from within the original triplet, which directly optimizes the positives without any mutual effect with the negatives. Extensive experiments show the combination of these two small redesigns can achieve unprecedented results: Our powerful and versatile triplet loss not only makes our model outperform all previous SoTA by a large margin, but also provides substantial performance boosts to a large number of existing models, while introducing no extra inference computation at all.
PDF Abstract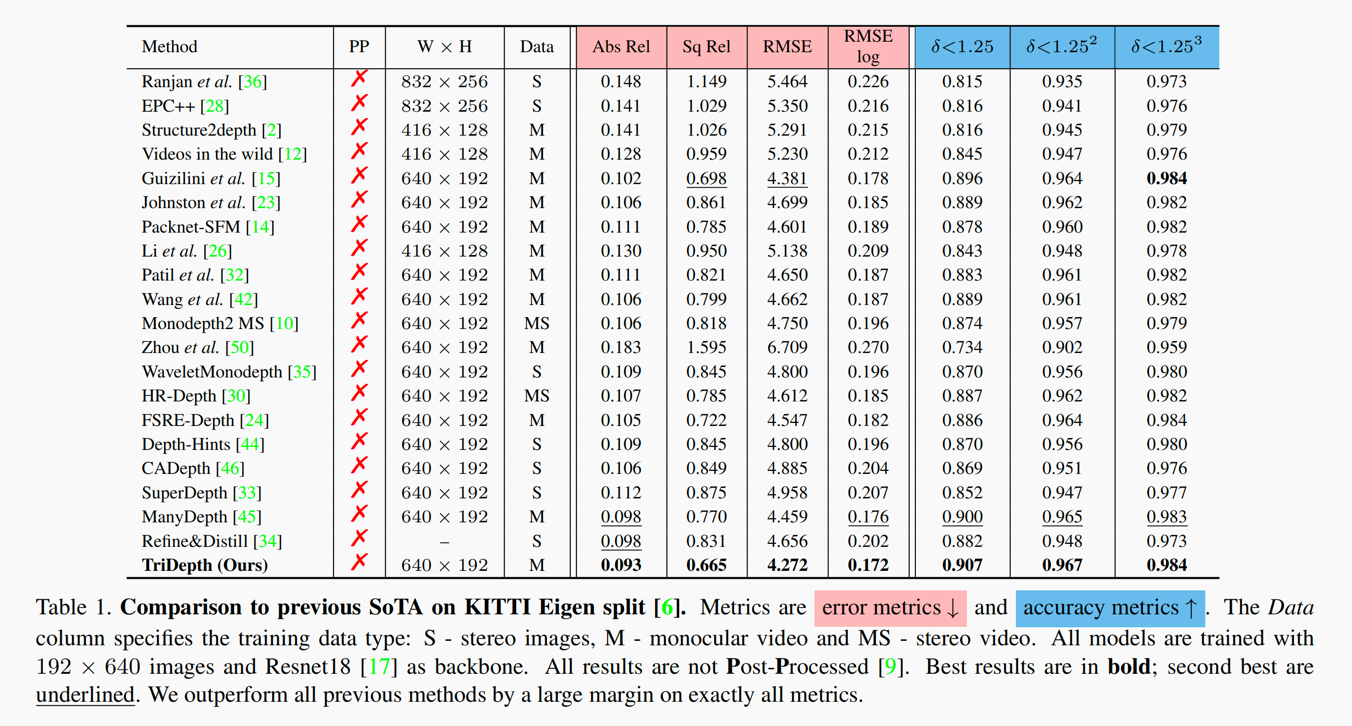







 KITTI
KITTI
