Toward Practical Monocular Indoor Depth Estimation
The majority of prior monocular depth estimation methods without groundtruth depth guidance focus on driving scenarios. We show that such methods generalize poorly to unseen complex indoor scenes, where objects are cluttered and arbitrarily arranged in the near field. To obtain more robustness, we propose a structure distillation approach to learn knacks from an off-the-shelf relative depth estimator that produces structured but metric-agnostic depth. By combining structure distillation with a branch that learns metrics from left-right consistency, we attain structured and metric depth for generic indoor scenes and make inferences in real-time. To facilitate learning and evaluation, we collect SimSIN, a dataset from simulation with thousands of environments, and UniSIN, a dataset that contains about 500 real scan sequences of generic indoor environments. We experiment in both sim-to-real and real-to-real settings, and show improvements, as well as in downstream applications using our depth maps. This work provides a full study, covering methods, data, and applications aspects.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2022 PDF CVPR 2022 Abstract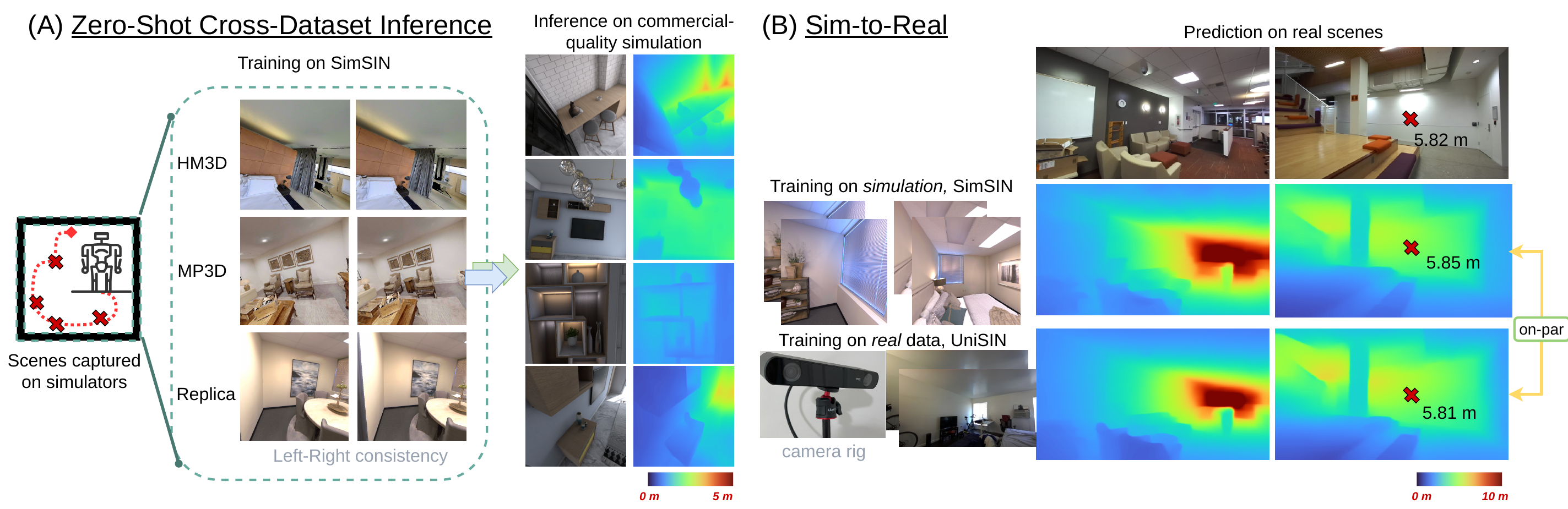





 VA (Virtual Apartment)
VA (Virtual Apartment)
 NYUv2
NYUv2
 Replica
Replica
 Hypersim
Hypersim
 HM3D
HM3D
