Zero-Shot Temporal Action Detection via Vision-Language Prompting
Existing temporal action detection (TAD) methods rely on large training data including segment-level annotations, limited to recognizing previously seen classes alone during inference. Collecting and annotating a large training set for each class of interest is costly and hence unscalable. Zero-shot TAD (ZS-TAD) resolves this obstacle by enabling a pre-trained model to recognize any unseen action classes. Meanwhile, ZS-TAD is also much more challenging with significantly less investigation. Inspired by the success of zero-shot image classification aided by vision-language (ViL) models such as CLIP, we aim to tackle the more complex TAD task. An intuitive method is to integrate an off-the-shelf proposal detector with CLIP style classification. However, due to the sequential localization (e.g, proposal generation) and classification design, it is prone to localization error propagation. To overcome this problem, in this paper we propose a novel zero-Shot Temporal Action detection model via Vision-LanguagE prompting (STALE). Such a novel design effectively eliminates the dependence between localization and classification by breaking the route for error propagation in-between. We further introduce an interaction mechanism between classification and localization for improved optimization. Extensive experiments on standard ZS-TAD video benchmarks show that our STALE significantly outperforms state-of-the-art alternatives. Besides, our model also yields superior results on supervised TAD over recent strong competitors. The PyTorch implementation of STALE is available at https://github.com/sauradip/STALE.
PDF Abstract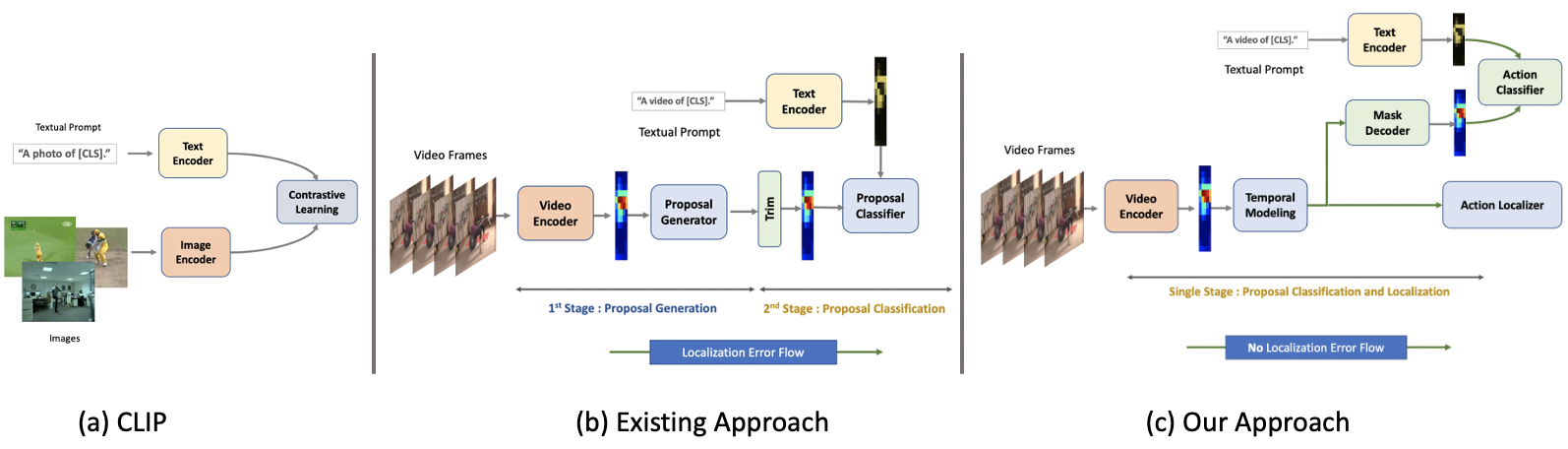







 ActivityNet
ActivityNet
 THUMOS14
THUMOS14
