Trending Research
Continual Learning of Large Language Models: A Comprehensive Survey
In this survey, we provide a comprehensive overview of the current research progress on LLMs within the context of CL.
Dynamic Generation of Personalities with Large Language Models
We propose a new metric to assess personality generation capability based on this evaluation method.
ESRL: Efficient Sampling-based Reinforcement Learning for Sequence Generation
Applying Reinforcement Learning (RL) to sequence generation models enables the direct optimization of long-term rewards (\textit{e. g.,} BLEU and human feedback), but typically requires large-scale sampling over a space of action sequences.
CharacterFactory: Sampling Consistent Characters with GANs for Diffusion Models
In this work, we propose CharacterFactory, a framework that allows sampling new characters with consistent identities in the latent space of GANs for diffusion models.
LGM: Large Multi-View Gaussian Model for High-Resolution 3D Content Creation
2) 3D Backbone: We present an asymmetric U-Net as a high-throughput backbone operating on multi-view images, which can be produced from text or single-view image input by leveraging multi-view diffusion models.
Metric3D v2: A Versatile Monocular Geometric Foundation Model for Zero-shot Metric Depth and Surface Normal Estimation
For metric depth estimation, we show that the key to a zero-shot single-view model lies in resolving the metric ambiguity from various camera models and large-scale data training.
 Ranked #1 on
Surface Normals Estimation
on NYU Depth v2
(using extra training data)
Ranked #1 on
Surface Normals Estimation
on NYU Depth v2
(using extra training data)
Retrieval Head Mechanistically Explains Long-Context Factuality
Despite the recent progress in long-context language models, it remains elusive how transformer-based models exhibit the capability to retrieve relevant information from arbitrary locations within the long context.
Diffusion Models and Semi-Supervised Learners Benefit Mutually with Few Labels
In an effort to further advance semi-supervised generative and classification tasks, we propose a simple yet effective training strategy called dual pseudo training (DPT), built upon strong semi-supervised learners and diffusion models.
Learning Visuotactile Skills with Two Multifingered Hands
Two significant challenges exist: the lack of an affordable and accessible teleoperation system suitable for a dual-arm setup with multifingered hands, and the scarcity of multifingered hand hardware equipped with touch sensing.
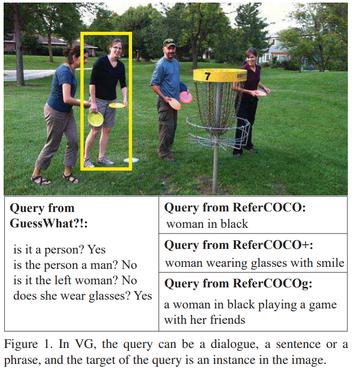
List Items One by One: A New Data Source and Learning Paradigm for Multimodal LLMs
Set-of-Mark (SoM) Prompting unleashes the visual grounding capability of GPT-4V, by enabling the model to associate visual objects with tags inserted on the image.
 Ranked #47 on
Visual Question Answering
on MM-Vet
Ranked #47 on
Visual Question Answering
on MM-Vet