Facial Landmark Points Detection Using Knowledge Distillation-Based Neural Networks
Facial landmark detection is a vital step for numerous facial image analysis applications. Although some deep learning-based methods have achieved good performances in this task, they are often not suitable for running on mobile devices. Such methods rely on networks with many parameters, which makes the training and inference time-consuming. Training lightweight neural networks such as MobileNets are often challenging, and the models might have low accuracy. Inspired by knowledge distillation (KD), this paper presents a novel loss function to train a lightweight Student network (e.g., MobileNetV2) for facial landmark detection. We use two Teacher networks, a Tolerant-Teacher and a Tough-Teacher in conjunction with the Student network. The Tolerant-Teacher is trained using Soft-landmarks created by active shape models, while the Tough-Teacher is trained using the ground truth (aka Hard-landmarks) landmark points. To utilize the facial landmark points predicted by the Teacher networks, we define an Assistive Loss (ALoss) for each Teacher network. Moreover, we define a loss function called KD-Loss that utilizes the facial landmark points predicted by the two pre-trained Teacher networks (EfficientNet-b3) to guide the lightweight Student network towards predicting the Hard-landmarks. Our experimental results on three challenging facial datasets show that the proposed architecture will result in a better-trained Student network that can extract facial landmark points with high accuracy.
PDF Abstract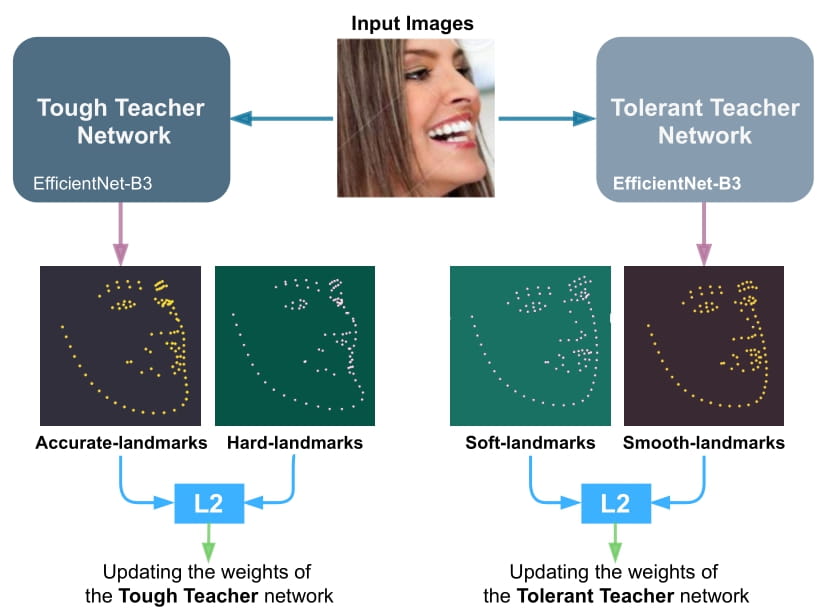





 300W
300W
 Helen
Helen
 LFPW
LFPW
 COFW
COFW
 WFLW
WFLW
