Text-image Alignment for Diffusion-based Perception
Diffusion models are generative models with impressive text-to-image synthesis capabilities and have spurred a new wave of creative methods for classical machine learning tasks. However, the best way to harness the perceptual knowledge of these generative models for visual tasks is still an open question. Specifically, it is unclear how to use the prompting interface when applying diffusion backbones to vision tasks. We find that automatically generated captions can improve text-image alignment and significantly enhance a model's cross-attention maps, leading to better perceptual performance. Our approach improves upon the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) in diffusion-based semantic segmentation on ADE20K and the current overall SOTA for depth estimation on NYUv2. Furthermore, our method generalizes to the cross-domain setting. We use model personalization and caption modifications to align our model to the target domain and find improvements over unaligned baselines. Our cross-domain object detection model, trained on Pascal VOC, achieves SOTA results on Watercolor2K. Our cross-domain segmentation method, trained on Cityscapes, achieves SOTA results on Dark Zurich-val and Nighttime Driving. Project page: https://www.vision.caltech.edu/tadp/. Code: https://github.com/damaggu/TADP.
PDF Abstract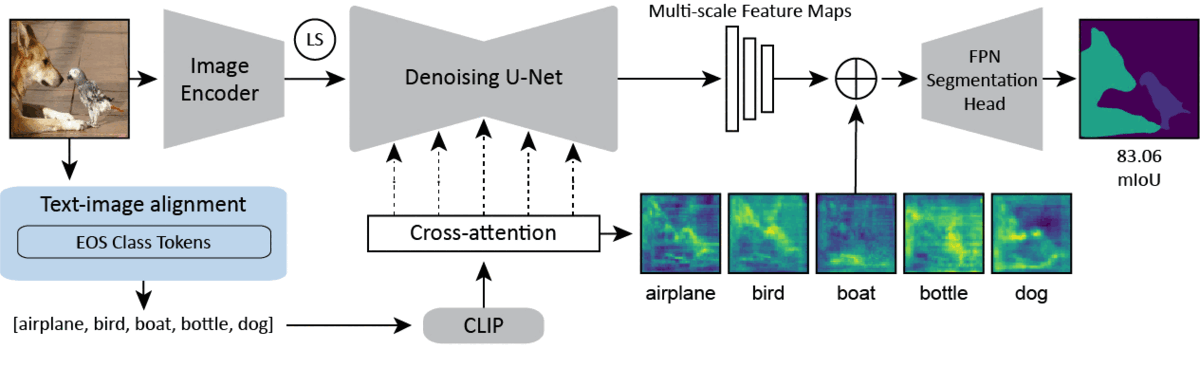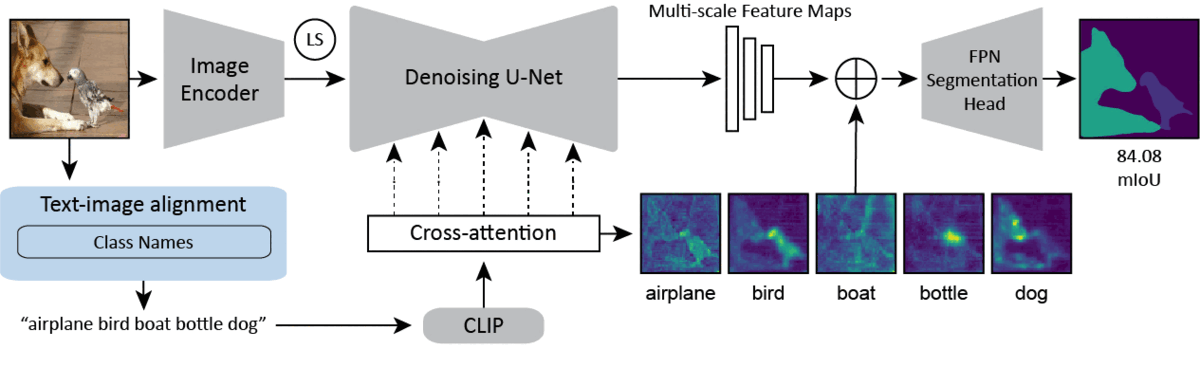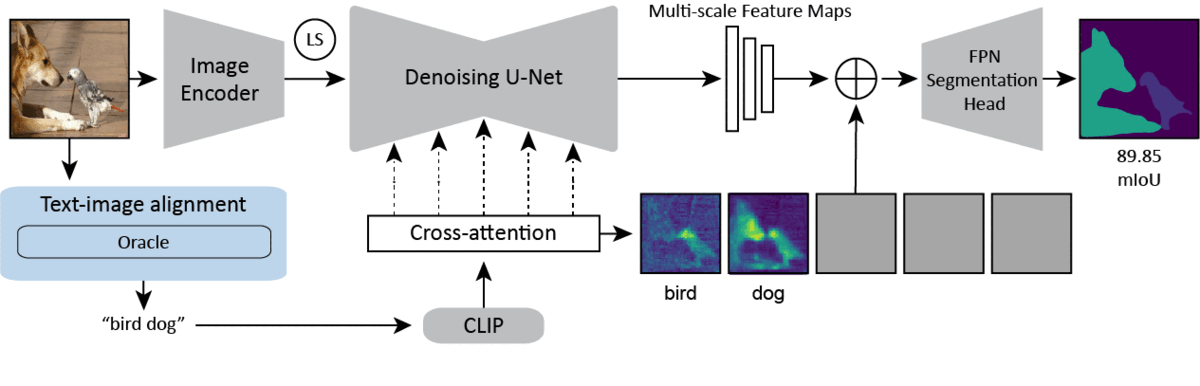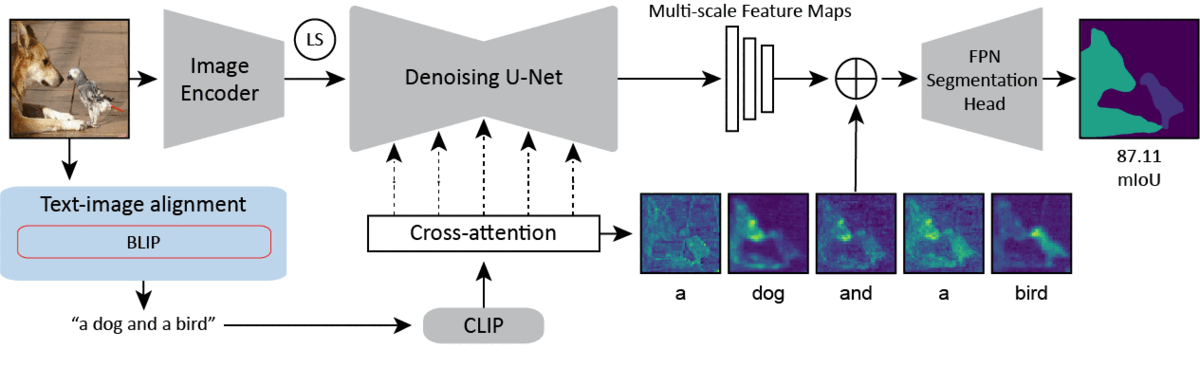













 Cityscapes
Cityscapes
 ADE20K
ADE20K
 NYUv2
NYUv2
 PASCAL VOC
PASCAL VOC
 Dark Zurich
Dark Zurich
 Comic2k
Comic2k
 Nighttime Driving
Nighttime Driving
