Wasserstein Distances for Stereo Disparity Estimation
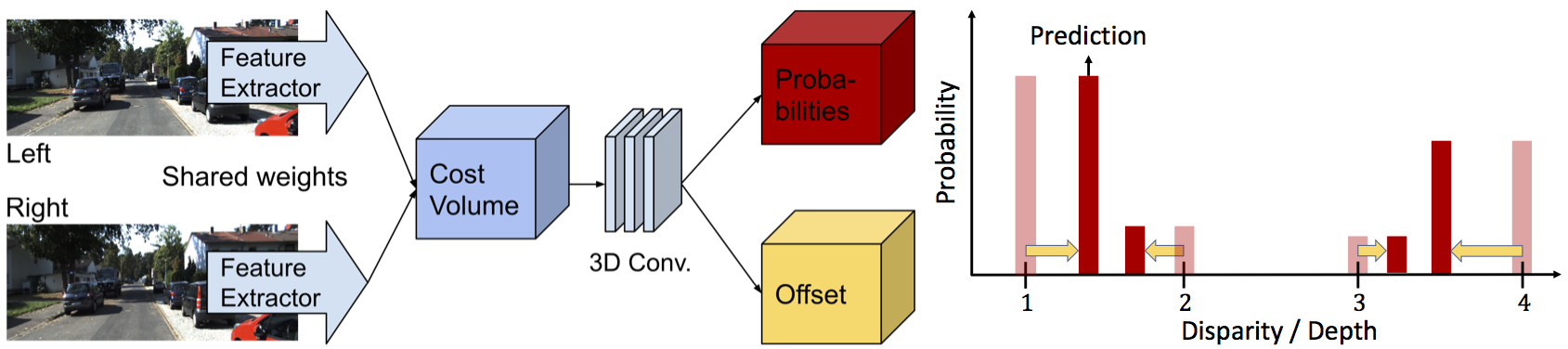
Existing approaches to depth or disparity estimation output a distribution over a set of pre-defined discrete values. This leads to inaccurate results when the true depth or disparity does not match any of these values. The fact that this distribution is usually learned indirectly through a regression loss causes further problems in ambiguous regions around object boundaries. We address these issues using a new neural network architecture that is capable of outputting arbitrary depth values, and a new loss function that is derived from the Wasserstein distance between the true and the predicted distributions. We validate our approach on a variety of tasks, including stereo disparity and depth estimation, and the downstream 3D object detection. Our approach drastically reduces the error in ambiguous regions, especially around object boundaries that greatly affect the localization of objects in 3D, achieving the state-of-the-art in 3D object detection for autonomous driving. Our code will be available at https://github.com/Div99/W-Stereo-Disp.
PDF Abstract NeurIPS 2020 PDF NeurIPS 2020 AbstractCode
Datasets
Results from the Paper
 Ranked #2 on
Stereo Depth Estimation
on KITTI2015
(three pixel error metric)
Ranked #2 on
Stereo Depth Estimation
on KITTI2015
(three pixel error metric)










 KITTI
KITTI